eclipse: This occurs when two celestial bodies line up in space so that one totally or partially obscures the other. In a solar eclipse, the sun, moon and Earth line up in that order. The moon casts its shadow on the Earth. From Earth, it looks like the moon is blocking out the sun. In a lunar eclipse, the three bodies line up in a different order — sun, Earth, moon — and the Earth casts its shadow on the moon, turning the moon a deep red.
electricity: A flow of charge, usually from the movement of negatively charged particles, called electrons.
fuel: Any material that will release energy during a controlled chemical or nuclear reaction. Fossil fuels (coal, natural gas and petroleum) are a common type that liberate their energy through chemical reactions that take place when heated (usually to the point of burning).
moon: The natural satellite of any planet.
solar: A word that describes anything about or coming from the sun. It comes from the Latin word for sun, sol.
solar eclipse: An event in which the moon passes between the Earth and sun and obscures the sun, at least partially. In a total solar eclipse, the moon appears to cover the entire sun, revealing on the outer layer, the corona. If you were to view an eclipse from space, you would see the moon’s shadow traveling in a line across the surface of the Earth.
solar energy: The energy in sunlight that can be captured as heat or converted into heat or electrical energy. Some people refer to wind power as a form of solar energy. The reason: Winds are driven by the variations in temperatures and the density of the air, both of which are affected by the solar heating of the air, ground and surface waters.
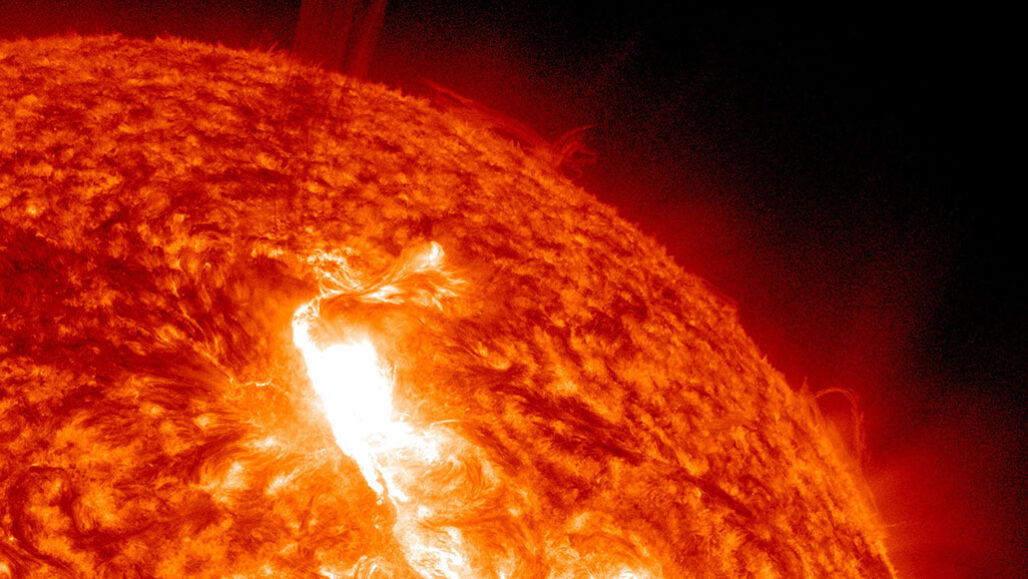
solar flare: An explosive event that takes place on the sun when energy that has built up in 'twisted' magnetic fields (usually above sunspots) becomes suddenly released. The energy can in minutes heat to many millions of degrees, emitting a burst of energy. That energy consists of radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum, from gamma rays to radio waves.
sun: The star at the center of Earth’s solar system. It is about 27,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Also a term for any sunlike star.