absolute zero The coldest possible temperature, also known as 0 kelvin. It is equal to minus 273.15 degrees Celsius (minus 459.67 degrees Fahrenheit).
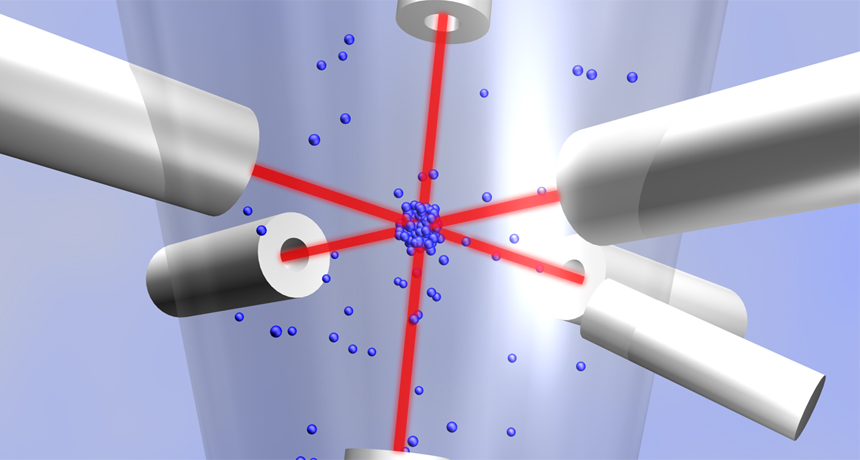
atom The basic unit of a chemical element. Atoms are made up of a dense nucleus that contains positively charged protons and neutrally charged neutrons. The nucleus is orbited by a cloud of negatively charged electrons.
atomic clock A timekeeping device that relies on the frequency of microwave emissions from excited cesium atoms. That frequency is 9,192,631,770 hertz (or cycles/oscillations per second). Many common devices including cell phones, computers and GPS-satellite receivers rely on the high accuracy of atomic clocks to regularly reset their time (known as synchronization).
cesium A metallic chemical element with the atomic number 55. Among its many uses, cesium serves as the basis of today’s atomic clocks and is used in many photo-electric cells.
electron A negatively charged particle; the carrier of electricity within solids. Atoms will have one or more of these orbiting around their nucleus.
frequency The number of times a specified periodic phenomenon occurs within a specified time interval. (In physics) The number of wavelengths that occurs over a particular interval of time.
laser A device that generates an intense beam of coherent light of a single color. Lasers are used in drilling and cutting, alignment and guidance, and in surgery.
microwaves An electromagnetic wave with a wavelength shorter than that of normal radio waves but longer than those of infrared radiation (heat) and of visible light.
NIST (short for National Institute of Standards and Technology) Created in 1901 as the National Bureau of Standards, this government agency is now part of the U.S. Department of Commerce. It is charged with figuring out the best or most accurate way to measure things and with developing new and more accurate ways to do that measuring. To develop and test those measurement technologies, this agency has maintained one of the oldest physical science laboratories in the United States. It actually maintains several laboratories, although its headquarters is in Gaithersburg, Md.
radiation Energy, emitted by a source, that travels through space in waves or as moving subatomic particles. Examples include visible light, infrared energy and microwaves.
vacuum (in science) Space with little or no matter in it.