Could Star Trek replicators exist?
Experts break down what’s possible and what’s not for this sci-fi invention
It’s not quite a replicator, but maybe future space travelers will be able to 3-D print dinner on demand.
REPLICATOR: WACOMKA/SHUTTERSTOCK; BACKGROUND: NOSOROGUA/SHUTTERSTOCK
Let’s say you’re hungry. Wouldn’t it be great to walk up to an appliance, tell it what food you want and have that food appear magically in front of your eyes? In the TV franchise Star Trek, this is possible with a piece of technology known as a “replicator.” Getting to a future where this tech exists, though, might take a bit of imagination and invention.
The Star Trek replicator is used to make all kinds of objects, from a hot cup of Earl Grey tea to spare parts for spaceships. Biowaste and other recycled material is broken down into basic parts: water, carbon and other molecules, explains Erin Macdonald. She’s an astrophysicist and science advisor for the Star Trek franchise. Those molecules are then fed into the replicator. When a person asks for an item, lasers reassemble the bits according to a recipe in the computer until it looks like that cup of tea, a dish of mint-chocolate-chip ice cream or a piece of a warp coil.
What, exactly, is the biowaste that goes into the machine? It will probably include poop, says Macdonald. “We don’t want to think about that too much.”

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
The replicator’s superfast lasers convert incoming matter into energy. Then, they change it back into matter. “On a fundamental level, there is nothing that prevents you from building a replicator-like machine,” says Gianluca Sarri. He’s a quantum physicist who works with lasers at Queen’s University Belfast in the United Kingdom.
But a replicator is just not a top priority at the moment, he says. All that conversion of matter to energy back to matter again would require a lot of energy. Plus, there’s no way to currently make an object appear within seconds. What’s more: Right now food can be generated in a much simpler way — by cooking.
Let’s print a meal
For now, astronauts eat food sent up from Earth. To make sure they get the food they need, future space tourists and crews might rely on hydroponics — growing plants without soil. Cooking that food in space like you do at home might be an option. But it might not always be practical inside the tight fit of a spaceship. So spacefarers might instead print that meal with a 3-D printer.
Today’s 3-D printers are similar to regular printers, notes Jonathan Blutinger. Just as normal printers must be fed cartridges of ink, 3-D printers must be fed cartridges of printing material. Blutinger is a design engineer.
While at the Creative Machines Lab at Columbia University in New York City, he helped create a 3-D printer that acts like a digital chef. “The printer will not allow you to make something from nothing,” he says. “You need to start with the right base ingredients.”
Blutinger’s group recently started with ingredients for a “cake.” They put graham-cracker paste, strawberry jam, peanut butter, Nutella, cherry drizzle, banana puree and frosting into the food printer. The printer assembled and cooked the ingredients with lasers to make a slice of cake.
The cake tasted great, Blutinger says, but it was definitely a unique experience because the flavors came in “waves.” The group’s paper about the cake appeared March 21 in npj Science of Food.
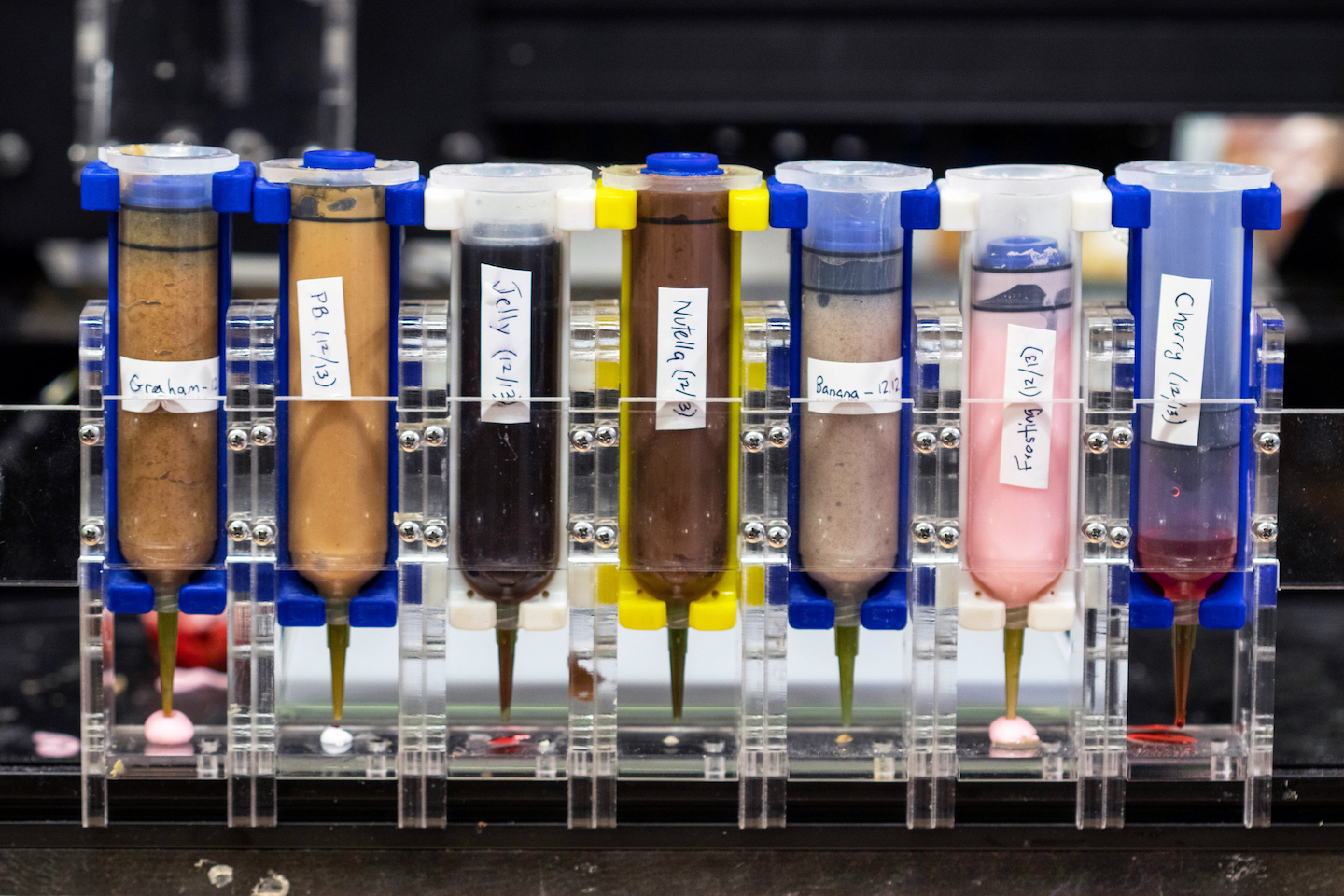

Appetizing or off-putting?
The 3-D printing robot chef can only assemble the ingredients it’s given and then add heat to cook the food. It cannot create foods from pure energy made from biowaste, like the fictional Star Wars replicator does. But people may not yet be comfortable eating even this relatively simple version of machine-made meals, Blutinger says.
Most people are comfortable with items like flour and peanut butter because we know where they come from. As science moves food away from the source, though, people could get grossed out. That 3-D printed cake might be easier for some to eat than 3-D printed meat, for instance. And people who did not grow up with 3-D printers in the kitchen might prefer food from the grocery store, Blutinger says.
“But pretty soon…kids will be growing up with these kinds of food robots in their kitchen,” he predicts. “Then that’s all they’re going to know.”
Macdonald agrees. “It’s just one of those things that people will have to come to terms with.”
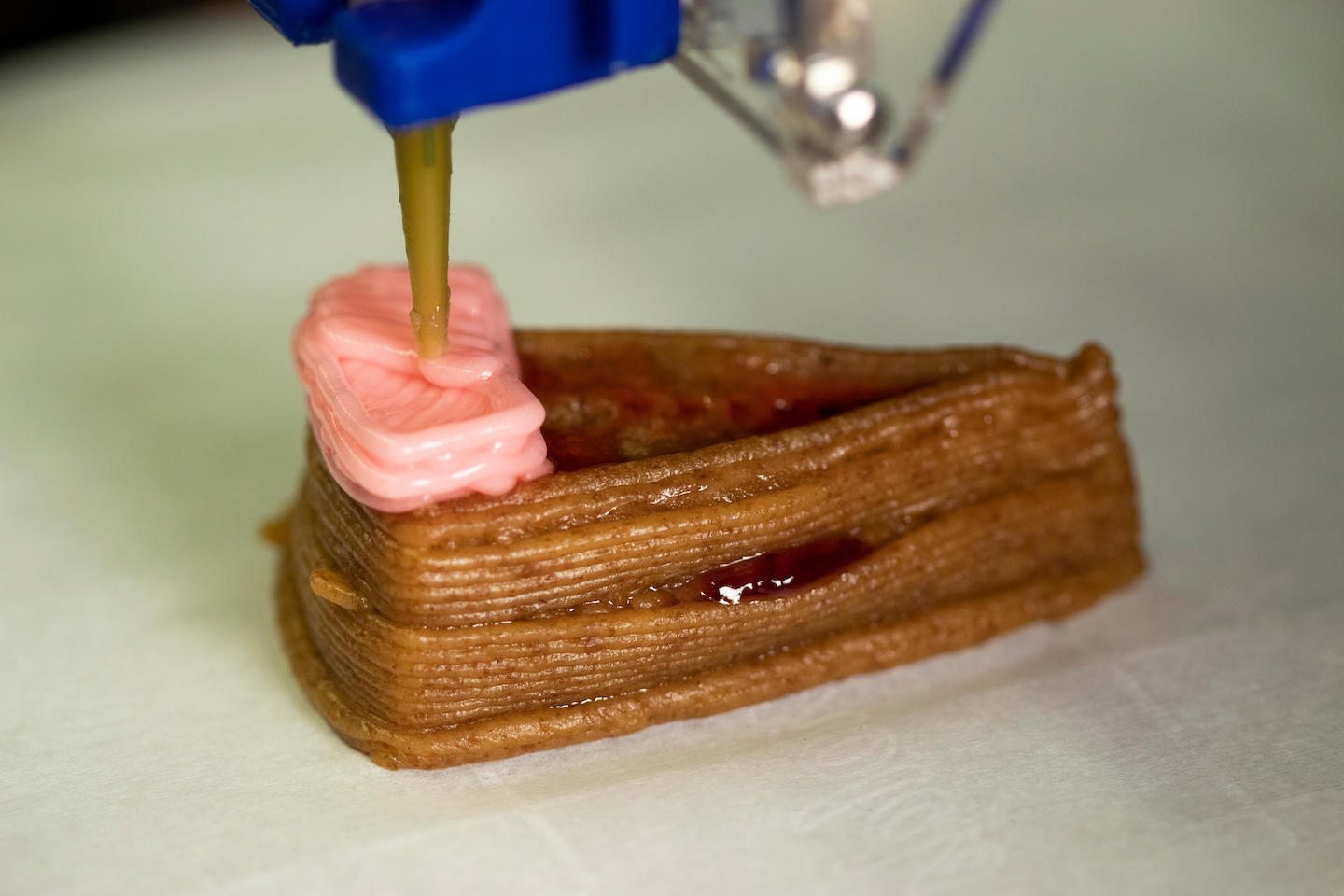
Food printers might be on our kitchen counters within the next 10 to 20 years, Sarri says. These printers could be like “having a personal chef and nutritionist all in one,” Blutinger adds. The machine could someday recommend and create healthier food that’s customized to your diet.
A Star Trek replicator might be possible, but not nearly as soon, says Sarri — maybe 100 years down the line. Those replicators of the future could be useful in areas in beyond outer space. They could provide food in places where putting a chef might be dangerous, such as a war zone.
“There’s a feedback loop,” Macdonald says, “of scientists being inspired by Star Trek and then making that science. And then that continues to feed into the science fiction of, ‘Well this is what we can do now, so what’s next?’”
The next tech to materialize might just be a replicator.