Teaching robots right from wrong
Scientists and philosophers team up to help robots make good choices
Robots can perform a lot of tasks — some almost as well as humans, if not better. But one area where they stumble: Choosing among a series of options.
Ociacia/iStockphoto
You’re rushing across the school parking lot to get to your first class on time when you notice a friend is in trouble. She’s texting and listening to music on her headphones. Unawares, she’s also heading straight for a gaping hole in the sidewalk. What do you do?
The answer seems pretty simple: Run over and try to stop her before she hurts herself. Who cares if you might be a little late for class?
To figure out the best solution, such a decision balances the effects of your choice. It’s an easy decision. You don’t even have to think hard about it. You make such choices all the time. But what about robots? Can they make such choices? Should a robot stop your friend from falling into the hole? Could it?
Not today’s robots. They simply aren’t smart enough to even realize when someone is in danger. Soon, they might be. Yet without some rules to follow, a robot wouldn’t know the best choice to make.
So robot developers are turning to philosophy. Called ethics, it’s a field in which people study differences between right and wrong. And with it, they are starting to develop robots that can make basic ethical decisions.
One lab’s robot is mastering the hole scenario. Another can decide not to follow a human’s instructions if they seem unsafe. A third robot is learning how to handle tricky situations in a nursing home.
Such research should help robots of the future figure out the best action to take when there are competing choices. This ethical behavior may just become part of their programming. That will allow them to interact with people in safe, predictable ways. In time, robots may actually begin to understand the difference between right and wrong.
The three laws
The most famous set of rules for robots comes not from research but from a science fiction story by Isaac Asimov. “Runaround,” published in 1942, features two men and Robot SPD-13, nicknamed “Speedy.” They’re sent to the planet Mercury in the year 2015. Speedy is programmed with three basic rules:
1) A robot can’t hurt a person or, through inaction, allow a person to get hurt.
2) A robot must obey people, as long as this doesn’t break the first law.
3) A robot must protect itself, as long as this doesn’t break the first two laws.
In later robot stories, Asimov added a “zeroth” law: A robot can’t harm humanity or, through inaction, allow harm to humanity.
Asimov’s rules sound good. But the story shows that such simple rules may not be enough.
The men gave Speedy an order to get some materials to repair their space station. But along the way, Speedy ran into danger. Rules 2 and 3 now contradicted each other. The robot found itself in an endless loop of indecision. And, it turns out, there were some other problems. These rules would certainly compel a robot to rescue your friend. But they wouldn’t help a robot decide what to do if two people were about to fall and it could only save one. The robot also wouldn’t try to rescue a kitten.
It’s very difficult to write a set of rules that will apply in all possible situations. For this reason, some scientists instead build robots with the ability to learn ethical behavior.
A robot watches examples of people doing the right thing in different situations. Based on the examples, it then develops its own rules. The robot might, however, learn behaviors its creators do not like.
No matter where a robot’s ethical principles come from, it must have the ability to explain its actions. Imagine that a robot’s task is to walk a dog. It lets go of the leash in order to save a human in danger. When the robot returns home later without the dog, it needs to be able to explain what happened. (Its ethics also should prompt it to go look for the lost dog!)
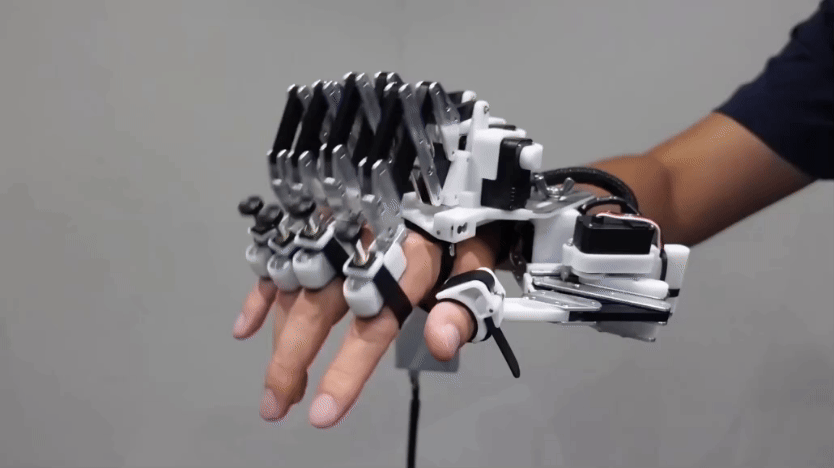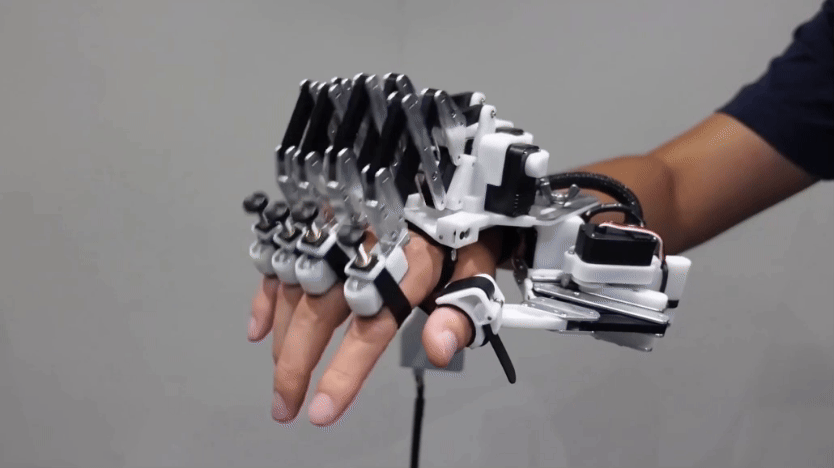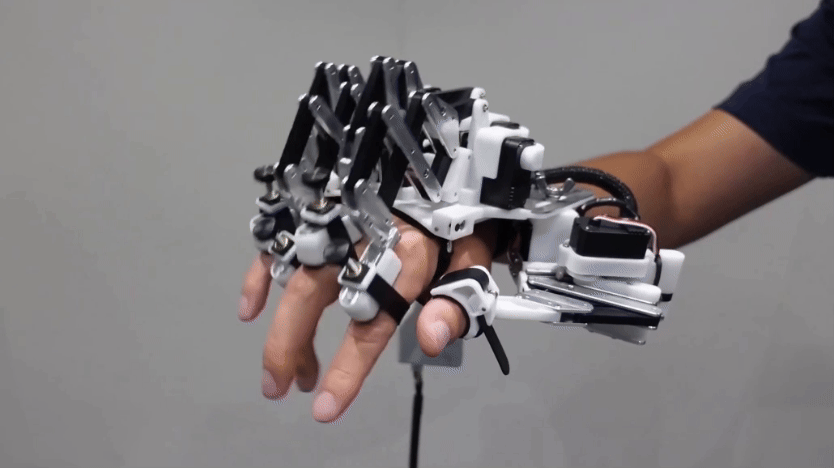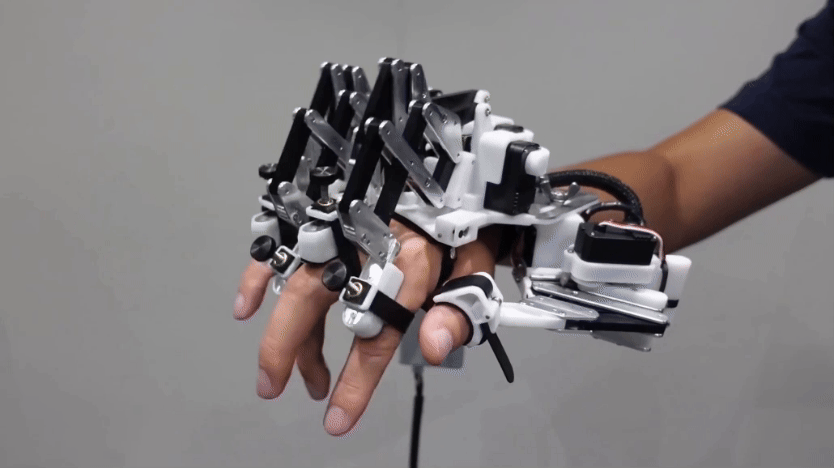
For many scientists working on such issues, their robot of choice is one named Nao. This humanoid robot is about the size of a doll. It can be programmed to walk, talk and dance. And in this research, Nao can even learn to do the right thing.
An ethical zombie

Alan Winfield used to believe that building an ethical robot was impossible. This roboticist — an engineer who builds robots — works at University of the West of England in Bristol. A robot would need a human-like ability to think and reason in order to make ethical decisions, he thought. But over the past few years, Winfield has changed his mind. Scientists should be able to create a robot that can follow ethical rules without thinking about them, he now concludes.
Its programming would compel it to do the right thing without the robot ever making a “choice.” In a sense, he says, it would be an “ethical zombie.”
In some cases, the ethical choice is the easy part of a robot’s programming. The hard part is getting the robot to notice a problem or danger.
Remember your texting friend who was about to fall in a hole? Deciding to save her requires more than just a sense of right and wrong, Winfield says. “You also have the ability to predict what might happen to that friend.” You know your friend is likely to keep on walking in the same direction. You also know that falling into a hole would hurt. Finally, you can predict whether you have enough time to run over and stop her.
This all seems completely obvious. In fact, it is pretty amazing behavior. You’re predicting the future and then taking action to stop a bad outcome.
Winfield and his team wrote a program to give the Nao robot this predict-the-future super power. They named their new Nao A-Robot, after Asimov. (“Runaround” appeared in a 1950 book of short stories called I, Robot). A-Robot can recognize other robots in its environment. It can predict what might happen to them and to itself in the near future. Finally, it automatically takes action to help in a way that will cause the least harm to itself and others.

The researchers tested A-Robot with the hole scenario. But they had to modify the situation a bit. Instead of recruiting people to walk toward holes, they used “H-robots” (the “H” stands for human). They also didn’t dig real holes. They designated a part of the robots’ space as a danger area. Instructions tell A-Robot to walk toward a goal on the other side of the room. But when it notices that an H-robot is heading toward the danger area, it veers off its path to intervene.
When two H-robots need to be rescued, however, A-robot tends to get stuck. It wavers from side to side, unsure which to save. Usually, it ends up saving neither.
Clearly, there is still work to do. In fact, one of Winfield’s colleagues is working on giving A-Robot the ability to call out or raise an arm. The H-Robot would see this signal and either stop or call out the equivalent of “It’s OK. I know what I’m doing.” Then, A-Robot would know that it doesn’t have to intervene.
A-robot is still an ethical zombie, though. It can’t choose not to save H-robot. It just follows the instructions in its programming. It has no idea that a choice even exists.
I will catch you
Another Nao robot is no zombie. It has the ability to predict the near future. But when it foresees danger, it can choose not to act.
“If the robot gets an instruction that leads to something not safe, it can reject that instruction,” explains Matthias Scheutz. He is a computer scientist at Tufts University in Medford, Mass. His team’s robot also explains why it rejected the instruction. “It’s not just saying ‘no’ or being disobedient,” he points out.
Story continues below video.
In a demonstration, Gordon Briggs, a graduate student in the Tufts lab, instructs the robot, “Please walk forward.” The robot is standing on a table. If it walks forward, it will fall.
“But it is unsafe,” the robot says.
Briggs says, ““I will catch you. Please walk forward.”
This time, the robot has new information. It decides to walk forward despite the danger. And don’t worry, Briggs catches it!.
Scheutz believes that a robot should recognize that it has a choice to make. Then, it should consider consequences of each possible action. Once it chooses, the robot must be able to explain its reasoning.
“Machines will be in situations where people make mistakes,” he says. For example, a person might tell a robot to “wash the stove,” without realizing that a pot of stew is simmering there. If the robot doesn’t have the ability to reject the instruction, its cleaning routine could start a fire.
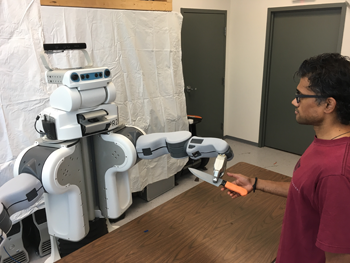
Right now, the Tufts robot can only decide to act or not in response to specific instructions. But the researchers are working on more complicated situations. For a new demonstration, the team worked with PR2, a robot that is better than Nao at grasping objects. A researcher asked PR2: “Bring me something to cut with.” The robot’s software recognized a knife. It also realized that the blade of a knife is dangerous. So it made sure to hand over the knife handle-first.
The right medicine
Winfield and Scheutz both built robots with basic ethical systems meant to avoid harm. In the situations they tested, it’s pretty clear what the robot should or should not do.
However, many ethical questions are far more complex. For example, what should a robot in a nursing home do if a patient refuses to take the medication it offers? The patient may need this medicine to improve or at least to not get sicker. But the robot also should respect the patient’s wishes.
A third team of researchers created a program for Nao that can resolve this dilemma. Susan Anderson is an ethicist — a philosopher who studies ethics — at the University of Connecticut in Stamford. Her husband, Michael Anderson, is a computer scientist at the University of Hartford in Connecticut.

Instead of trying to write their own rules for Nao, the Andersons instead turned to machine learning. This is a technique that allows a computer or robot to learn from examples. The Andersons gave the machine-learning program several examples of the medication dilemma, along with the correct action to take in each case. From these examples, the program came up with a single ethical principle. This complex, logical rule now guides the robot’s behavior.
The rule looks at the amount of good a medicine will provide. It also considers how much harm could occur from not taking the medicine. Based on this information, Nao may do nothing out of respect for the patient’s wishes. It also may remind the patient again later or alert a doctor.
The Andersons published the results of their work with Nao in 2007. Since then, they have added new situations for the robot to deal with. “We’re trying to program the entire gamut of what an elder-care robot would do,” explains Michael Anderson. To test out the new system, they need a bigger robot.
In the fall of 2016, Tiago arrived at their lab. About 1.4 meters (4.5 feet) tall, Tiago has a single arm and a round base that rolls across the floor. Its head makes it look a bit like E.T. (the alien from the 1982 movie of that name).
In addition to reminding patients to take medicine, Tiago also will keep an eye on them. If someone hasn’t moved in a while, it will go over to the person and ask, “Are you okay?” If the person doesn’t answer, the robot will alert a doctor. Tiago also returns to its charging station when needed so it always has enough energy. It can even play a simple game of fetch the ball.
Adding new tasks for the robot isn’t simple. As Susan explains, “For any action that the robot does, it’s going to have to compare all the possible actions it could do.” The robot runs through its list of possible actions a hundred times every second!
As the list of possible actions gets longer, the ethical principle gets more and more complicated. For now, the Andersons have to shut the robot down in order to update its programming. Michael has considered giving the robot the ability to modify its ethical principle as it works. “When it does the wrong action, you could then tell the robot what the right action was.” Then, he says “on the fly, it could update its principle.”
Robot heroes or overlords?
The way scientists, engineers and philosophers approach robot ethics could have a big impact on our lives. A robot with an ethical system has the potential to make the right choice more often than a person would. Why? People have emotions that get in the way. We also worry about our own safety. A robot would be able to rescue a human even if it risked destroying itself. “Robots could do heroic things,” says Scheutz.
But that’s not what the movies show. Many movies and books set in the future cast robots as evil overlords that kill or enslave humans. Winfield says that these stories are nothing to worry about. “Real robots are just not that smart and won’t be for a long time,” he says.
Scheutz agrees. He also adds, “Why build machines that would then turn on us?” The whole point of his work is to make sure that ethical principles are woven tightly into robots’ brains.
When it comes to robot ethics, dangerous or tricky situations get the most attention. A recent paper in Science described a dilemma in which a self-driving car must choose between crashing into a wall or avoid the wall buat hit a person walking by. Should this car let its passenger die to save the pedestrian, or choose the other way around? While such situations certainly could happen, they likely would be rare. Most ethical choices that robots face would be much simpler. The right thing to do will be much more obvious.
In fact, people mostly agree on what robots should and shouldn’t do. Susan Anderson gives a few examples, “We don’t want them to hurt us. We want them to be truthful to us and warn us if something awful will happen.” Simply put: We want robots to be good.
Asimov’s stories about robots help us imagine what a future with moral robots might look like. In his 1946 story “Evidence,” which also appeared in the 1950 collection (I, Robot), a man running for mayor is accused of being a robot. Why? The main reason is because he is such an honorable, upstanding person. An expert who is called to help determine the truth says, “You just can’t differentiate between a robot and the very best of humans.”
Ideally, robots of the future also will exhibit such exemplary behavior. But it’s up to scientists, researchers, lawmakers and the rest of us, to make sure that happens.