Scientists Say: Endocytosis
This is what happens when a cell needs to take in something big
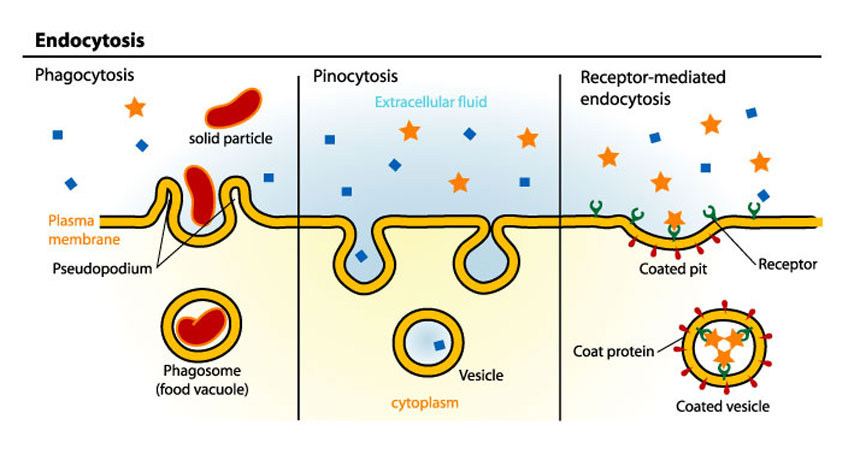
When a cell membrane folds around a substance outside of the cell, this is called endocytosis.
Mariana Ruiz Villarreal LadyofHats/Wikimedia Commons
This is what happens when a cell needs to take in something big

When a cell membrane folds around a substance outside of the cell, this is called endocytosis.
Mariana Ruiz Villarreal LadyofHats/Wikimedia Commons