atom The basic unit of a chemical element. Atoms are made up of a dense nucleus that contains positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons. The nucleus is orbited by a cloud of negatively charged electrons.
decay (for radioactive materials) The process whereby a radioactive isotope — which means a physically unstable form of some element — sheds energy and subatomic particles. In time, this shedding will transform the unstable element into a slightly different but stable element. For instance, uranium-238 (which is a radioactive, or unstable, isotope) decays to radium-222 (also a radioactive isotope), which decays to radon-222 (also radioactive), which decays to polonium-210 (also radioactive), which decays to lead-206 — which is stable. No further decay occurs. The rates of decay from one isotope to another can range from timeframes of less than a second to billions of years.
element (in chemistry) Each of more than one hundred substances for which the smallest unit of each is a single atom. Examples include hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, lithium and uranium.
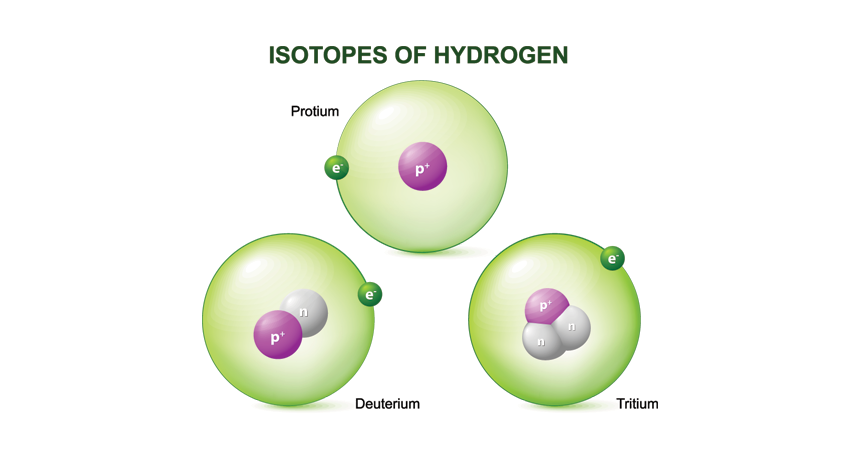
isotope Different forms of an element that vary somewhat in mass (and potentially in lifetime). All have the same number of protons but different numbers neutrons in their nucleus.
moon The natural satellite of any planet.
neutron A subatomic particle carrying no electric charge that is one of the basic pieces of matter. Neutrons belong to the family of particles known as hadrons.
nucleus Plural is nuclei. (in biology) A dense structure present in many cells. Typically a single rounded structure encased within a membrane, the nucleus contains the genetic information. (in astronomy) The rocky body of a comet, sometimes carrying a jacket of ice or frozen gases. (in physics) The central core of an atom, containing most of its mass.
particle A minute amount of something.
planet A celestial object that orbits a star, is big enough for gravity to have squashed it into a roundish ball and has cleared other objects out of the way in its orbital neighborhood. To accomplish the third feat, the object must be big enough to have pulled neighboring objects into the planet itself or to have slung them around the planet and off into outer space. Astronomers of the International Astronomical Union (IAU) created this three-part scientific definition of a planet in August 2006 to determine Pluto’s status. Based on that definition, IAU ruled that Pluto did not qualify. The solar system now includes eight planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
proton A subatomic particle that is one of the basic building blocks of the atoms that make up matter. Protons belong to the family of particles known as hadrons.