angle The space (usually measured in degrees) between two intersecting lines or surfaces at or close to the point where they meet.
density The measure of how condensed some object is, found by dividing its mass by its volume.
glass A hard, brittle substance made from silica, a mineral found in sand. Glass usually is transparent and fairly inert (chemically nonreactive). Aquatic organisms called diatoms build their shells of it.
Plexiglas or plexiglass The first is the trademarked name (the second is a more general name) for the chemical poly(methyl methacrylate) . It’s a transparent plastic that can resist shattering. It can be used in place of glass for many applications.
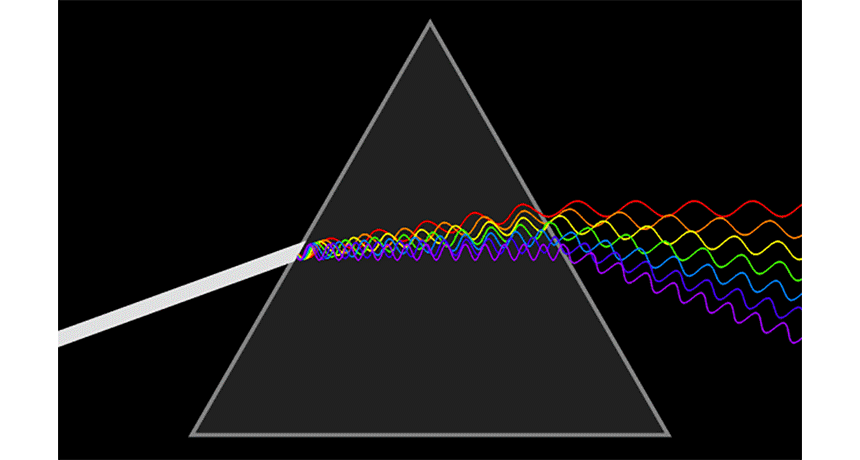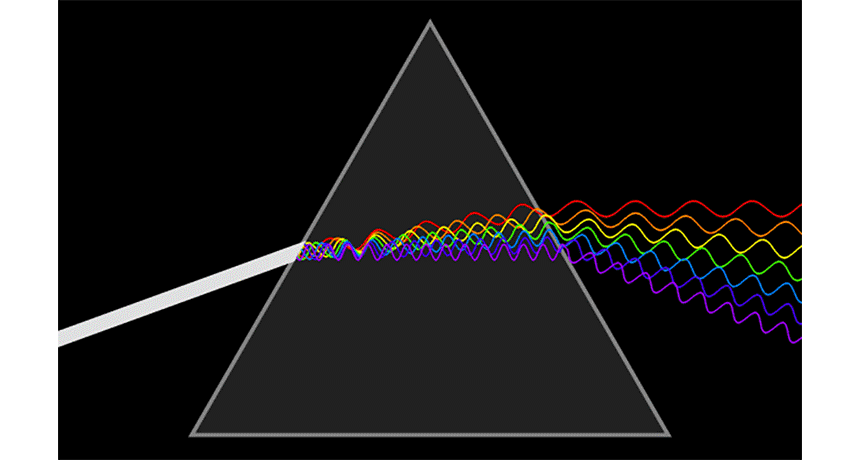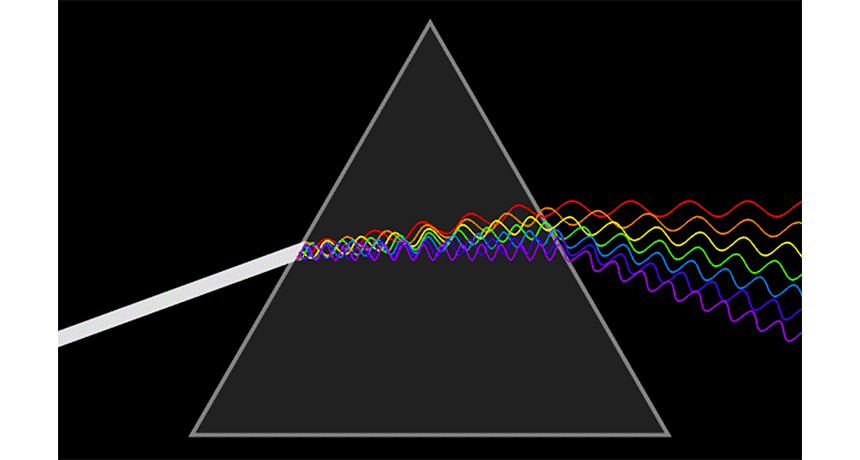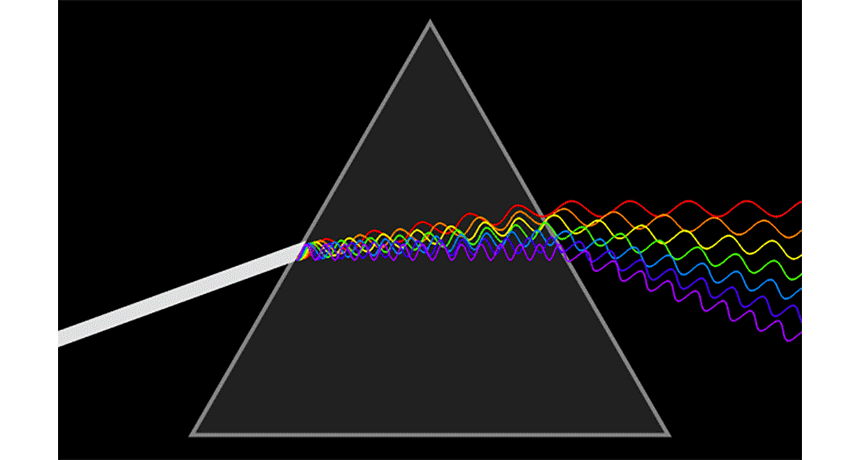
prism A triangular wedge of glass or another clear substance that can bend the components of white light into a rainbow-like succession of colored bands.
rainbow An arc of color displayed across the sky during or just after a rain. It’s caused when water droplets in the atmosphere bend (or diffract) white sunlight into a number of its component hues: usually red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet.
refraction The change in direction of light (or any other wave) as it passes through some material. For example, the path of light leaving water and entering air will bend, making partially submerged objects to appear to bend at the water’s surface.
sound wave A wave that transmits sound. Sound waves have alternating swaths of high and low pressure.
transparent Allowing light to pass through so that objects behind can be distinctly seen.
wave A disturbance or variation that travels through space and matter in a regular, oscillating fashion.
wavelength The distance between one peak and the next in a series of waves, or the distance between one trough and the next. Visible light — which, like all electromagnetic radiation, travels in waves — includes wavelengths between about 380 nanometers (violet) and about 740 nanometers (red). Radiation with wavelengths shorter than visible light includes gamma rays, X-rays and ultraviolet light. Longer-wavelength radiation includes infrared light, microwaves and radio waves.
wood A porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees, shrubs and other woody plants.