astronomy The area of science that deals with celestial objects, space and the physical universe. People who work in this field are called astronomers.
comet A celestial object consisting of a nucleus of ice and dust. When a comet passes near the sun, gas and dust vaporize off the comet’s surface, creating its trailing “tail.”
Neptune The furthest planet from the sun in our solar system. It is the fourth largest planet in the solar system.
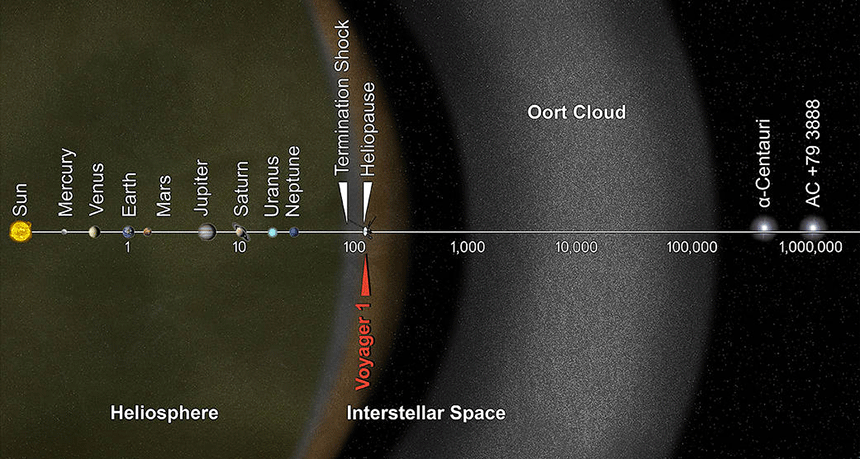
Oort cloud A swarm of small rocky and icy bodies far beyond the orbit of Pluto, up to 1.5 light-years from the sun. The cloud is a source of some comets.
orbit The curved path of a celestial object or spacecraft around a star, planet or moon. One complete circuit around a celestial body.
Pluto A dwarf planet that is located in the Kuiper Belt, just beyond Neptune. Pluto is the tenth largest object orbiting the sun.
solar system The eight major planets and their moons in orbit around our sun, together with smaller bodies in the form of dwarf planets, asteroids, meteoroids and comets.
star The basic building block from which galaxies are made. Stars develop when gravity compacts clouds of gas. When they become dense enough to sustain nuclear-fusion reactions, stars will emit light and sometimes other forms of electromagnetic radiation. The sun is our closest star.
sun The star at the center of Earth’s solar system. It’s an average size star about 26,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Also a term for any sunlike star.
trillion A number representing a million million — or 1,000,000,000,000 — of something.