atom The basic unit of a chemical element. Atoms are made up of a dense nucleus that contains positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons. The nucleus is orbited by a cloud of negatively charged electrons.
chemical A substance formed from two or more atoms that unite (bond) in a fixed proportion and structure. For example, water is a chemical made when two hydrogen atoms bond to one oxygen atom. Its chemical formula is H2O. Chemical also can be an adjective to describe properties of materials that are the result of various reactions between different compounds.
crust (in geology) Earth’s outermost surface, usually made from dense, solid rock.
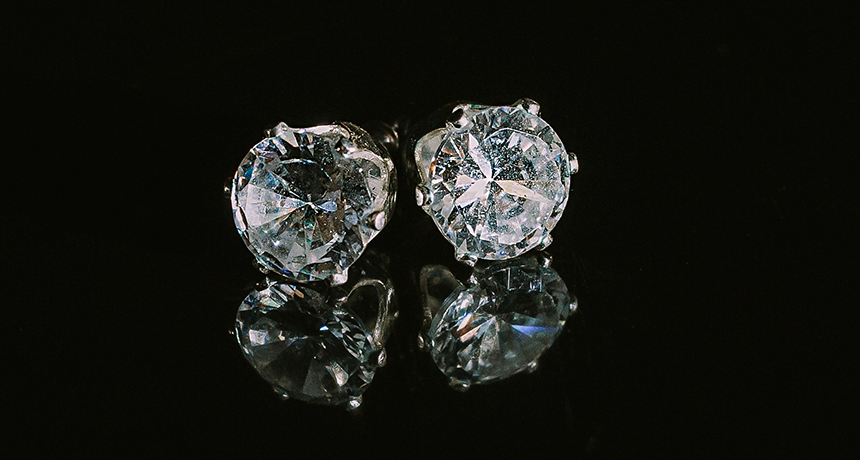
diamond One of the hardest known substances and rarest gems on Earth. Diamonds form deep within the planet when carbon is compressed under incredibly strong pressure.
Earth’s crust The outermost layer of Earth. It is relatively cold and brittle.
element A building block of some larger structure. (in chemistry) Each of more than one hundred substances for which the smallest unit of each is a single atom. Examples include hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, lithium and uranium.
iron A metallic element that is common within minerals in Earth’s crust and in its hot core. This metal also is found in cosmic dust and in many meteorites.
metal Something that conducts electricity well, tends to be shiny (reflective) and malleable (meaning it can be reshaped with heat and not too much force or pressure).
moon The natural satellite of any planet.
oxygen A gas that makes up about 21 percent of Earth's atmosphere. All animals and many microorganisms need oxygen to fuel their growth (and metabolism).
radiation (in physics) One of the three major ways that energy is transferred. (The other two are conduction and convection.) In radiation, electromagnetic waves carry energy from one place to another. Unlike conduction and convection, which need material to help transfer the energy, radiation can transfer energy across empty space.
zirconium A metallic element that is often used in structures needed to withstand high temperatures and radiation (such as nuclear reactors).