All Stories
-
 Humans
HumansGot back-to-school COVID-19 questions? We’ve got answers
If everybody masks up at school, that could prevent a bumpy 2021–22 schoolyear. It also could keep safe those students too young to be vaccinated.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceScientists Say: Aerosol
Aerosols are tiny bits of solids or drops of liquids suspended in gas. Aerosols include mist, fog and soot, as well as pollution from fossil fuels.
-
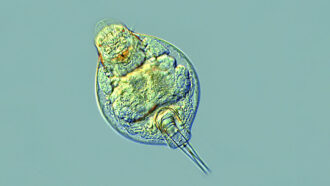 Animals
AnimalsTiny animals survive 24,000 years in suspended animation
Tiny bdelloid rotifers awake from a 24,000-year slumber when freed from the Arctic permafrost.
-
 Life
LifeSome pikas survive winter by eating yak poop
Pikas endure bone-chilling cold on the Tibetan Plateau by using little energy and fueling up on yak poop.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentWildfire smoke seeds the air with potentially dangerous microbes
Studies now show that most wildfires don’t kill microbes. That’s fueling worries about what risks these smoke hitchhikers might pose to people.
By Megan Sever -
 Physics
PhysicsTake a look at this weird, bendy type of ice
These specially grown threads of ice bend into curves, then spring back when released.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAnalyze This: Sharks aren’t as scary as what you see on TV
In Shark Week shows, scientists found mixed messages about sharks, insufficient research support and little info on conserving endangered animals.
-
 Tech
TechLet’s learn about artificial intelligence
Computers are getting smarter all the time. At some tasks, they can even outsmart people.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineKids lost more than learning when COVID closed their schools
The first 18 months of the pandemic has already taken a hefty academic and emotional toll on students, new research shows.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Oxidation and Reduction
Oxidation and reduction are two parts of a chemical process in which one atom steals electrons from another.
-
 Space
SpaceThis image may be the first look at exomoons in the making
These observations offer some of the best evidence yet that planets around other stars have moons, or exomoons.
-
 Tech
TechHeadphones or earmuffs could replace needles in some disease testing
A new system that uses earmuffs to collect gases coming out the skin could help doctors diagnose a variety of diseases, scientists say.
By Sid Perkins