All Stories
-
 Psychology
PsychologyDone right, online learning might be as engaging as face-to-face
Measures of stress offer clues to how engaged students are during online lessons. This could help teachers design more effective classes.
-
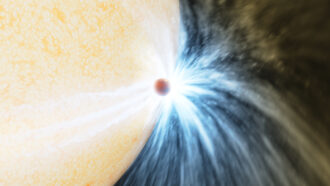 Planets
PlanetsIn a first, telescopes have caught a star eating a planet
A burst of light and a cloud of dust are signs that a distant star swallowed a giant planet.
-
 Plants
PlantsCould a plant ever eat a person?
For now, humans aren’t on the menu for carnivorous plants. But what would it take for one to consume a person?
-
 Environment
EnvironmentFungi help rescue crops being harmed by microplastics
Microplastics in the soil hinder plant growth. But two finalists at Regeneron ISEF found that fungi and farm waste can reduce the harm.
-
 Brain
BrainScientists Say: Addiction
Recovering from addiction is hard but possible. Encouragement of loved ones can improve a person’s chances of overcoming this disease.
-
 Fossils
FossilsThis ancient bird rocked a head like a T. rex
This bird from 120 million years ago had a head like a dinosaur and a body more like today’s birds.
-
 Space
SpaceJames Webb telescope catches newborn stars sculpting spiral galaxies
Dark voids riddle the galaxies, revealing new details about how stars alter their environments.
-
 Fossils
FossilsAncient jellyfish? Upside down this one looks like something else
A new look at an ancient sea animal called Essexella suggests it may have been a type of burrowing sea anemone, not a floating jelly.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Physics
PhysicsExplainer: Reflection, refraction and the power of lenses
The inner workings of microscopes, telescopes, eyeglasses and other lens-based devices rely on two important laws of optics.
By Trisha Muro -
 Tech
TechNanocrystal ‘painted’ films may someday help relieve summer heat
The rainbow palette and cooling powers of new plant-based films comes from their microscopic surface patterns of tiny crystals.
-
 Tech
TechA device spots and counts honeybees hosting a dangerous parasite
At Regeneron ISEF, three teens debuted an infrared system to detect honeybees carrying mites. It can show beekeepers when a colony needs to be treated.
-
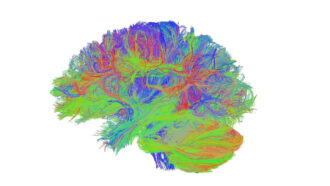 Brain
BrainScientists Say: Connectome
A connectome is a diagram of the cellular highways that carry information in the brain.