Scientists Say
A weekly word defined, in a sentence and in context.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists Say: Lymph
Lymph is a colorless fluid that bathes the body’s tissues and mops up bacteria, viruses and wastes.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceScientists Say: Crystal
The atoms or molecules in crystals take on a particular, repeatable pattern.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyScientists Say: Mummy
Mummies are dead bodies that don’t rot. They can form under natural conditions or because of chemicals that stop decay.
-
 Life
LifeScientists Say: Zooxanthellae
Algae called zooxanthellae live in the tissue of coral and provide the coral with food and its color.
-
 Space
SpaceScientists Say: Galaxy
A galaxy is a group of millions to billions of stars, plus a lot of dust and gas.
-
 Animals
AnimalsScientists Say: Extinction
When the last member of a species dies, it’s gone forever. That species is extinct.
-
 Chemistry
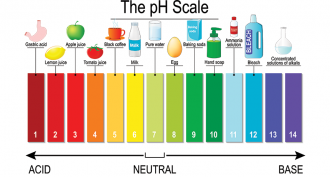
ChemistryScientists Say: pH
pH is a scale used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. The scale ranges from zero to 14, with seven as the perfect neutral middle.
-

Scientists Say: Mineral
Minerals are chemical elements or compounds that form repeating crystal structures. Quartz is a mineral. Table salt is, too.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists Say: Olfactory
Smell something? Thank your olfactory sense. Olfactory refers to anything having to do with smell.
-
 Animals
AnimalsScientists Say: Hertz
Frequency is how often something repeats over a period of time. Frequency is often measured in hertz, the number of times a cycle repeats each second.
-
 Physics
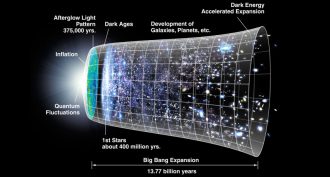
PhysicsScientists Say: Big Bang
The Big Bang is the current theory about how our universe came to be. It began with a vast explosion of matter — a very Big Bang.
By Bethany Brookshire and Trisha Muro -
 Life
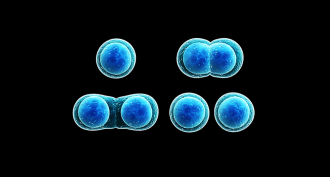
LifeScientists Say: Mitosis
Mitosis is a type of cell division where one cell divides into two identical copies, called daughter cells.