Drugs and zzzzzz’s
People who take the drug ecstasy are more likely to suffer from a sleeping disorder
People who take the illegal drug called ecstasy report feelings of great happiness or well-being while they’re high, but those same people may be finding it hard to breathe when they sleep. When a person stops breathing while sleeping and has to gasp for air, that’s called sleep apnea. And a new study found that regular users of ecstasy are more likely to suffer from sleep apnea than people who had never touched the drug.
Sleep apnea can cause a wide variety of other problems, including headaches, drowsiness and low energy. It is also linked to more serious problems like stroke and heart disease. Sleep apnea occurs when the muscles in the throat become too relaxed and block the airway.
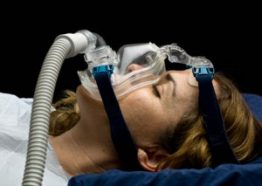
The scientists watched the people as they slept and counted the number of times per hour they stopped breathing. Based on this count, the scientists rated sleep apnea as mild, moderate or severe. For mild sleep apnea, the scientists found almost no difference between the groups.
But for more serious sleep apnea, a dangerous difference showed up. None of the people in the first group suffered from any serious sleep apnea, but 8 people in the second group—the group of ecstasy users—did have moderate sleep apnea. One of the ecstasy users had severe sleep apnea.
In addition, the scientists found that the more ecstasy that people had taken, the more likely they were to have serious sleep apnea.
Sigrid Veasey is a doctor who studies the science of sleep but did not work on this study. She told Science News that “the results are intriguing.” Veasey points out that this experiment brings up an important and unanswered question: Are young people who have sleep apnea more likely to use ecstasy, or does the use of ecstasy somehow cause bad cases of sleep apnea?
In other words, even though there’s a strong connection between ecstasy use and sleep apnea, the researchers did not show that ecstasy causes sleep apnea. The connection shown by this experiment is called correlation. Two things are said to have a correlation when they tend to change together.
If the sleep apnea can be blamed on ecstasy itself, the reason for the connection might be in neurons, the cells that transmit signals through the brain and central nervous system. Some types of neurons make a chemical called serotonin, which helps control many processes in the human body, including mood, appetite and sleep. Previous studies suggest that ecstasy is harmful to the neurons that make serotonin, so people who take ecstasy may not be getting all the serotonin they need.
Veasey, who works at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine in Philadelphia, has studied the connection between serotonin and sleep apnea in dogs.
She found that when serotonin is blocked, dogs suffered from worse sleep apnea than dogs with normal serotonin. She told Science News that mild sleep apnea in young people could get worse if their serotonin is blocked—say, by a drug like ecstasy.
These studies suggest that during sleep, the drug causes anything but “ecstasy.” The word “ecstasy,” apart from the drug, is used to describe a strong and overwhelming emotional state. In other words, ecstasy is like extreme happiness—the exact opposite of what most people feel if they haven’t gotten enough sleep.
POWER WORDS (adapted from the Yahoo! Kids Dictionary and Merriam Webster online, www.m-w.com)
central nervous system The portion of the vertebrate nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord.
neuron Any of the impulse-conducting cells that constitute the brain, spinal column, and nerves.
serotonin An organic compound found in animal and human tissue, especially the brain, blood serum, and gastric mucous membranes. Serotonin is active as a neurotransmitter and in vasoconstriction, stimulation of the smooth muscles, and regulation of cyclic body processes.
ecstasy A synthetic drug used illicitly for its mood-enhancing and hallucinogenic properties. Also called MDMA, which stands for methylenedioxymethamphetamine.
sleep apnea A temporary suspension of breathing occurring repeatedly during sleep that often affects overweight people or those having an obstruction in the breathing tract, an abnormally small throat opening, or a neurological disorder.







