cell: (in biology) The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism. Typically too small to see with the unaided eye, it consists of a watery fluid surrounded by a membrane or wall. Depending on their size, animals are made of anywhere from thousands to trillions of cells.
epilepsy: (adj. epileptic) A neurological disorder characterized by seizures.
link: A connection between two people or things.
mammal: An animal distinguished by possessing hair or fur, the secretion of milk by females for the feeding of their young, and (typically) the bearing of live young. They also are warm-blooded (or endothermic).
model: A simulation of a real-world event (usually using a computer) that has been developed to predict one or more likely outcomes. Or an individual that is meant to display how something would work in or look on others.
neuroscientist: Someone who studies the structure or function of the brain and other parts of the nervous system.
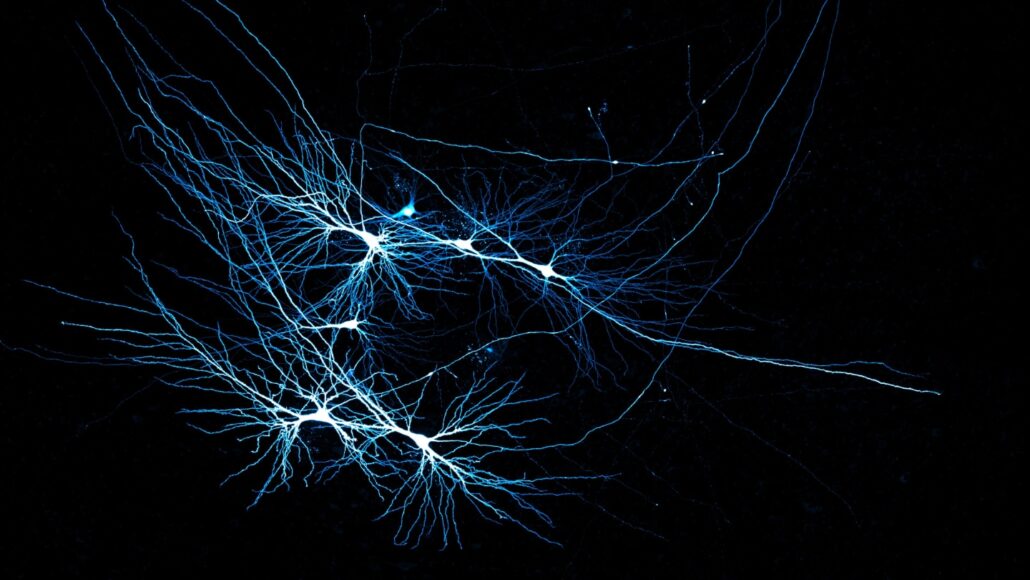
pyramidal cell: A type of brain neuron that has a bushy branch of hair-like dendrites that extend out from its cell body. These dendrites collect signals from their neural neighbors.
recall: To remember.
rodent: A mammal of the order Rodentia, a group that includes mice, rats, squirrels, guinea pigs, hamsters and porcupines.
synapse: The junction between neurons that transmits chemical and electrical signals.
technology: The application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes, especially in industry — or the devices, processes and systems that result from those efforts.
unique: Something that is unlike anything else; the only one of its kind.