Cellulose may keep ice cream from turning gritty in your freezer
It should keep ice crystals from growing as they melt and refreeze, tests show

Ice cream left in the freezer for too long can turn grainy as large ice crystals form. Researchers found a way to keep those crystals small.
American Heritage Chocolate/Unsplash
By Anna Gibbs
You can never have too much ice cream. But ice cream can become too icy. This happens when the ice crystals in that treat get too big, turning it gritty. Researchers now offer a way to prevent that.
Ice cream contains tiny ice crystals. As that dessert sits in your freezer, crystals in it will gradually grow bigger. This is partly because of tiny temperature changes in the freezer, explains Richard Hartel. He’s a food engineer at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, who was not involved in the new research. The freezer starts to warm a trifle over time (which is why the motor will turn on again), even if you haven’t opened its door.
This warming lets the ice melt a bit before it cools again and refreezes. Small crystals melt more quickly than larger ones. And when they reform, they tend to do so as bigger, grittier-tasting crystals. Only if the ice cream is kept really frigid, Hartel says — as in below –40º Celsius (or Fahrenheit) — will its ice crystals stay frozen and tiny.
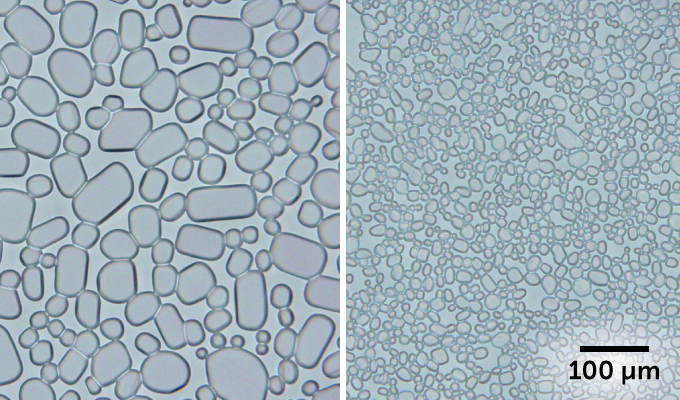
To help limit the crystals’ growth, companies add substances called stabilizers to ice cream. These are usually gums (such as guar or locust bean gum). And while these help, they don’t completely stop ice crystal growth. Once those ice crystals hit 50 micrometers (0.0002 inch) in diameter, the ice cream tastes coarse and gritty.
Some frogs and other animals produce protein molecules that stop ice crystals from growing. These “antifreeze” proteins help them survive subzero temperatures. The proteins work by sticking to the surface of ice crystals so that they can’t grow. Antifreeze proteins work better than gums. They also are quite costly.
Tao Wu is a food scientist at the University of Tennessee in Knoxville. He and his team have been trying to find better ice cream stabilizers. They’ve found that cellulose nanocrystals, or CNCs, look promising. Made from processed wood, they cost far less than antifreeze proteins.
In one experiment, the scientists added CNCs to a sugar solution (as an ice cream stand-in). After 24 hours, the ice crystals completely stopped growing. A week later, the ice crystals were still no bigger than 25 micrometers — so they wouldn’t taste gritty. When they used a gum instead of the CNCs, the crystals grew to more than 50 micrometers in just three days.
“That by itself suggests that nanocrystals are a lot more potent than the gums,” says Hartel. If CNCs work like antifreeze proteins, they may be a better stabilizer, he says. But more research is needed to confirm that.
Wu’s team reported its findings at the American Chemical Society meeting in San Diego, Calif. on March 20.
Until such new stabilizers make it into the marketplace, you still have a good excuse to eat your family’s ice cream quickly.







