agriculture: The growth of plants, animals or fungi for human needs, including food, fuel, chemicals and medicine.
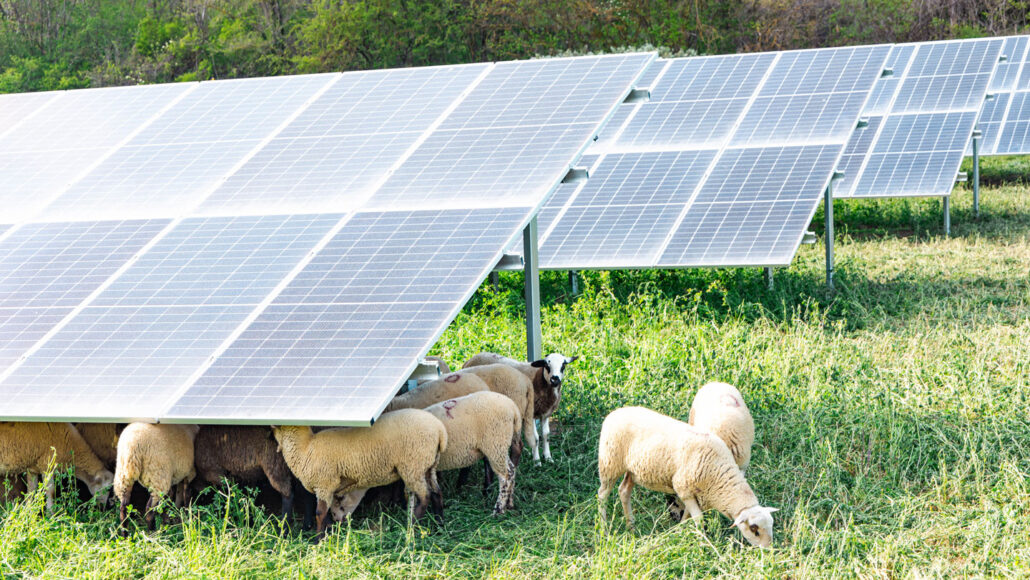
agrivoltaics: It's a type of mixed agriculture that combines the production of food (plant crops and/or livestock) with electricity. The term is a mashup of agriculture and photovoltaics (materials — such as solar panels — that generate electric current from sunlight).
crop: (in agriculture) A type of plant grown intentionally grown and nurtured by farmers, such as corn, coffee or tomatoes. Or the term could apply to the part of the plant harvested and sold by farmers.
herb: A seed-making plant that does not produce long-lived woody stems or branches (as a shrub or tree does), but instead dies down to the ground at the end of the growing season. (in cooking and medicine) The plant or part of a plant valued for its scent, flavor or therapeutic properties.
insect: A type of arthropod that as an adult will have six segmented legs and three body parts: a head, thorax and abdomen. There are hundreds of thousands of insects, which include bees, beetles, flies and moths.
livestock: Animals raised for meat or dairy products, including cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, chickens and geese. In some cases, farmed insects are referred to as mini-livestock.
moisture: Small amounts of water present in the air, as vapor. It can also be present as a liquid, such as water droplets condensed on the inside of a window, or dampness present in clothing or soil.
photovoltaic: An adjective that describes the ability of certain technologies to convert sunlight into electricity.
pollinate: To transport male reproductive cells — pollen — to female parts of a flower. This allows fertilization, the first step in plant reproduction.
solar: Having to do with the sun or the radiation it emits. It comes from sol, Latin for sun.
solar energy: The energy in sunlight that can be captured as heat or converted into heat or electrical energy. Some people refer to wind power as a form of solar energy. The reason: Winds are driven by the variations in temperatures and the density of the air, both of which are affected by the solar heating of the air, ground and surface waters.
sun: The star at the center of Earth’s solar system. It is about 27,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Also a term for any sunlike star.
technology: The application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes, especially in industry — or the devices, processes and systems that result from those efforts.