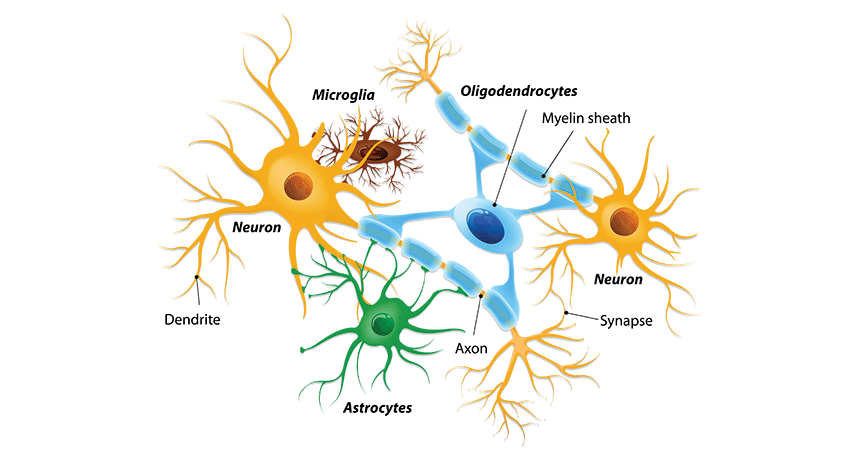
astrocyte A type of non-nerve cell found in the brain.
cell The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism. Typically too small to see with the unaided eye, it consists of a watery fluid surrounded by a membrane or wall. Depending on their size, animals are made of anywhere from thousands to trillions of cells. Most organisms, such as yeasts, molds, bacteria and some algae, are composed of only one cell.
diet The foods and liquids ingested by an animal to provide the nutrition it needs to grow and maintain health. (verb) To adopt a specific food-intake plan for the purpose of controlling body weight.
glia Non-nerve cells, these make up about half of the cells in the brain. Some glial cells wrap around axons. This speeds the rate of neural signaling and helps prevent confusing “cross-talk” between neighboring nerve cells. Other glial cells provide nutrients and oxygen to neurons, or defend the nervous system from injury.
glue A sticky substance that attaches one material to another.
immune (adj.) Having to do with the immunity. (v.) Able to ward off a particular infection. Alternatively, this term can be used to mean an organism shows no impacts from exposure to a particular poison or process. More generally, the term may signal that something cannot be hurt by a particular drug, disease or chemical.
immune system The collection of cells and their responses that help the body fight off infections and deal with foreign substances that may provoke allergies.
infection A disease that can spread from one organism to another. It’s usually caused by some type of germ.
microglia A type of cell found in the brain and spinal cord. It can move from place to place, and serve as part of the immune system, protecting the brain from infection.
nerve A long, delicate fiber that transmits signals across the body of an animal. An animal’s backbone contains many nerves, some of which control the movement of its legs or fins, and some of which convey sensations such as hot, cold or pain.
nervous system The network of nerve cells and fibers that transmits signals between parts of the body.
neuron An impulse-conducting cell. Such cells are found in the brain, spinal column and nervous system.
oxygen A gas that makes up about 21 percent of Earth's atmosphere. All animals and many microorganisms need oxygen to fuel their growth (and metabolism).