artery: Part of the body’s circulation system. There are several. Each is a major tube running between the heart and blood vessels that will move blood to all parts of the body.
bladder: A flexible bag-like structure for holding liquids. (in biology) The organ that collects urine until it will be excreted.
blood pressure: The force exerted against vessel walls by blood moving through the body. Usually this pressure refers to blood moving specifically through the body’s arteries. That pressure allows blood to circulate to our heads and keeps the fluid moving so that it can deliver oxygen to all tissues. Blood pressure can vary based on physical activity and the body’s position. High blood pressure can put someone at risk for heart attacks or stroke. Low blood pressure may leave people dizzy, or faint, as the pressure becomes too low to supply enough blood to the brain.
blood vessel: A tubular structure that carries blood through the tissues and organs.
chronic: A condition, such as an illness (or its symptoms, including pain), that lasts for a long time.
crystal: (adj. crystalline) A solid consisting of a symmetrical, ordered, three-dimensional arrangement of atoms or molecules. It’s the organized structure taken by most minerals. Apatite, for example, forms six-sided crystals. A rock's crystalline components are usually too small to be seen with the unaided eye.
diabetes: A disease where the body either makes too little of the hormone insulin (known as type 1 disease) or ignores the presence of too much insulin when it is present (known as type 2 diabetes).
dialysis: The removal of waste from blood by a machine as a substitute for the normal function of a kidney.
extract: (v.) To separate one chemical (or component of something) from a complex mix. (noun) A substance, often in concentrated form, that has been removed from some source material. Extracts are often taken from plants (such as spearmint or lavender), flowers and buds (such as roses and cloves), fruit (such as lemons and oranges) or seeds and nuts (such as almonds and pistachios). Such extracts, sometimes used in cooking, often have very strong scents or flavors.
filter: (n.) Something that allows some materials to pass through but not others, based on their size or some other feature. (v.) The process of screening some things out on the basis of traits such as size, density, electric charge. (in physics) A screen, plate or layer of a substance that absorbs light or other radiation or selectively prevents the transmission of some of its components.
filtration: The process of using a fabric, screen or some other type of material — known as filters — to prevent something from moving through. Drapes can limit the filtration of sunlight into a room. A wire mesh can filter large particles from water or the air. Sand or soils can provide filtration to keep some waterborne chemicals or germs from reaching groundwater.
function: The specific role some structure or device plays. (in math) A relationship between two or more variables in which one variable (the dependent one) is exactly determined by the value of the other variables.
high blood pressure: The common term for a medical condition known as hypertension. It puts a strain on blood vessels and the heart.
hormone: (in zoology and medicine) A chemical produced in a gland and then carried in the bloodstream to another part of the body. Hormones control many important body activities, such as growth. Hormones act by triggering or regulating chemical reactions in the body. (in botany) A chemical that serves as a signaling compound that tells cells of a plant when and how to develop, or when to grow old and die.
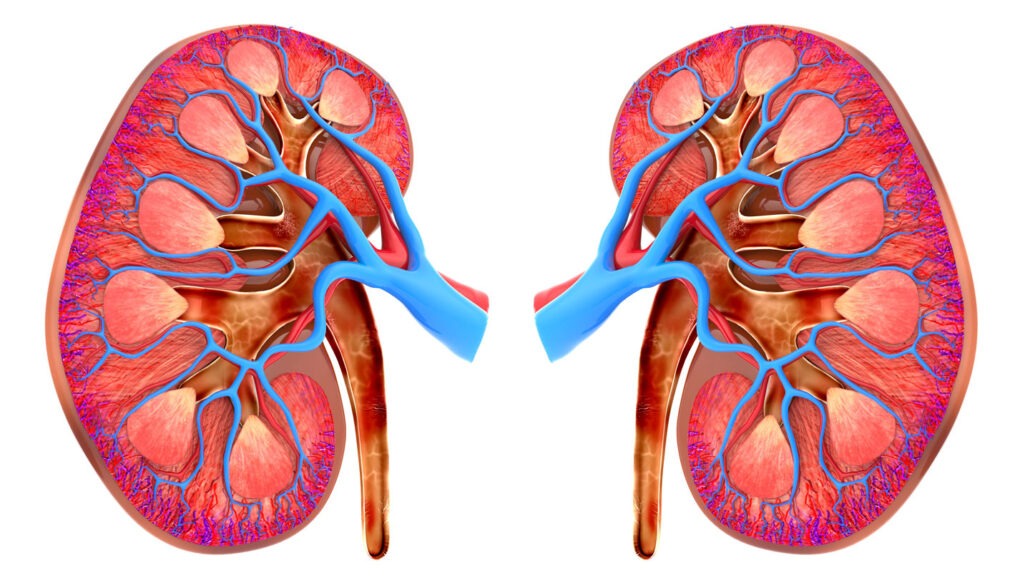
kidney: Each in a pair of organs in mammals that filters blood and produces urine.
mineral: Crystal-forming substances that make up rock, such as quartz, apatite or various carbonates. Most rocks contain several different minerals mish-mashed together. A mineral usually is solid and stable at room temperatures and has a specific formula, or recipe (with atoms occurring in certain proportions) and a specific crystalline structure (meaning that its atoms are organized in regular three-dimensional patterns). (in physiology) The same chemicals that are needed by the body to make and feed tissues to maintain health.
muscle: A type of tissue used to produce movement by contracting its cells, known as muscle fibers. Muscle is rich in protein, which is why predatory species seek prey containing lots of this tissue.
nephron: One of the blood-filtering units that the body's two kidneys use to remove fluids and wastes. In people, each kidney may have about one million of these. Each nephron consists of a filtering structure — called a glomerulus — and an attached tube-shaped structure.
organ: (in biology) Various parts of an organism that perform one or more particular functions. For instance, an ovary is an organ that makes eggs, the brain is an organ that makes sense of nerve signals and a plant’s roots are organs that take in nutrients and moisture.
renal: Adjective for things having to do with the kidneys.
salt: A compound made by combining an acid with a base (in a reaction that also creates water). The ocean contains many different salts — collectively called “sea salt.” Common table salt is a made of sodium and chlorine.
smoking: A term for the deliberate inhalation of tobacco smoke from burning cigarettes.
ureter: One of several thin, tubelike structures that connects the kidneys to the bladder. This system allows the body to store urine and the wastes it carries until there is enough to trigger urination.
vein: (in zoology) Part of a body’s circulation system. These tubes usually carry blood toward the heart.
waste: Any materials that are left over from biological or other systems that have no value, so they can be disposed of as trash or recycled for some new use.