algae Single-celled organisms, once considered plants (they aren’t). As aquatic organisms, they grow in water. Like green plants, they depend on sunlight to make their food.
crustaceans Hard-shelled water-dwelling animals including lobsters, crabs and shrimp.
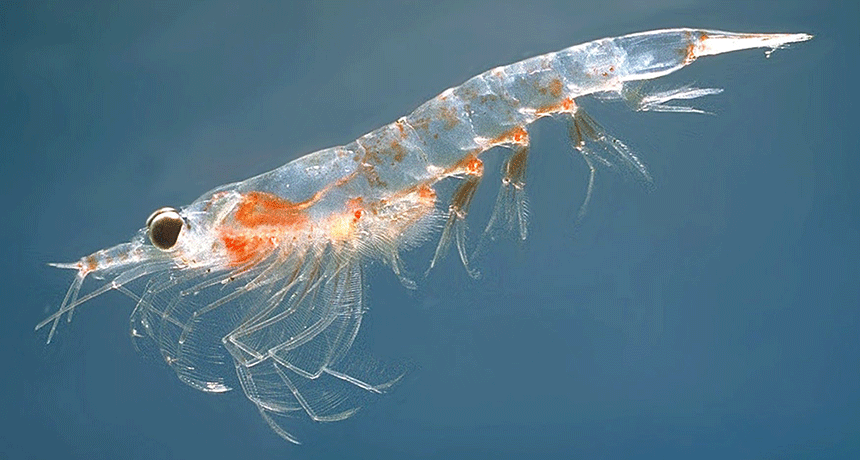
krill Tiny shrimplike crustaceans that live in the ocean and are the main food source of some whales.
nutrient A vitamin, mineral, fat, carbohydrate or protein that a plant, animal or other organism requires as part of its food in order to survive.
penguin flightless black-and-white bird native to the far Southern Hemisphere, especially Antarctica and its nearby islands.
phytoplankton Sometimes referred to as microalgae, these are microscopic plants and plant-like organisms that live in the ocean. Most float and reside in regions where sunlight filters down. Much like land-based plants, these organisms contain chlorophyll. They also require sunlight to live and grow. Phytoplankton serve as a base of the oceanic food web.
sea An ocean (or region that is part of an ocean). Unlike lakes and streams, seawater — or ocean water — is salty.
squid A member of the cephalopod family (which also contains octopuses and cuttlefish). These predatory animals, which are not fish, contain eight arms, no bones, two tentacles that catch food and a defined head. The animal breathes through gills. It swims by expelling jets of water from beneath its head and then waving finlike tissue that is part of its mantle, a muscular organ. Like an octopus, it may mask its presence by releasing a cloud of “ink.”
swarm A large number of animals that have amassed and now move together. People sometimes use the term to refer to huge numbers of honeybees leaving a hive.
whale A common, but fairly imprecise, term for a class of large mammals that lives in the ocean. This group includes dolphins and porpoises.