adenosine A molecule in the body made from a sugar bound to a nitrogen-based material. It helps the body transport energy in molecules such as ATP. It also promotes sleep in people.
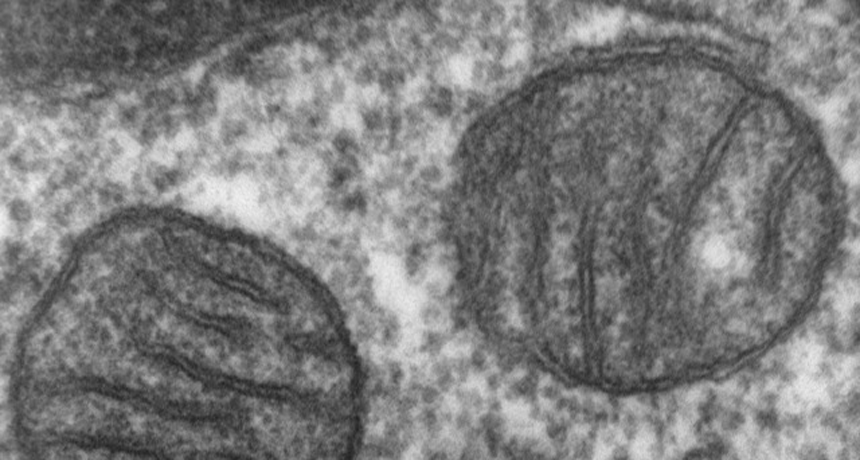
adenosine triphosphate (ATP) This is a molecule that cells make to power almost all of their activities. Cells use oxygen and simple sugars to create this molecule, the main source of their energy. The small structures in cells that carry out this energy-storing process are known as mitochondria. Like a battery, ATP stores a bit of usable energy. Once the cell uses it up, mitochondria must recharge the cell by making more ATP using energy harvested from the cell’s nutrients.
bacteria ( singular: bacterium ) Single-celled organisms. These dwell nearly everywhere on Earth, from the bottom of the sea to inside other living organisms (such as plants and animals).
cell The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism. Typically too small to see with the unaided eye, it consists of a watery fluid surrounded by a membrane or wall. Depending on their size, animals are made of anywhere from thousands to trillions of cells. Some organisms, such as yeasts, molds, bacteria and some algae, are composed of only one cell.
DNA (short for deoxyribonucleic acid) A long, double-stranded and spiral-shaped molecule inside most living cells that carries genetic instructions. It is built on a backbone of phosphorus, oxygen, and carbon atoms. In all living things, from plants and animals to microbes, these instructions tell cells which molecules to make.
glucose A simple sugar that is an important energy source in living organisms. As an energy source moving around the bloodstream, it may be known as “blood sugar.” It is half of the molecule that makes up table sugar (also known as sucrose).
liver An organ of the body of animals with backbones that performs a number of important functions. It can store fat and sugar as energy, break down harmful substances for excretion by the body, and secrete bile, a greenish fluid released into the gut, where it helps digest fats and neutralize acids.
mitochondria (sing. mitochondrion ) Structure in all cells (except bacteria and archaea) that break down nutrients and convert them into a form of energy known as ATP.
nutrient A vitamin, mineral, fat, carbohydrate or protein that a plant, animal or other organism requires as part of its food in order to survive.
red blood cell Colored red by hemoglobin, these cells move oxygen from the lungs to all tissues of the body. Red blood cells are too small to be seen by the unaided eye.