DNA (short for deoxyribonucleic acid) A long, double-stranded and spiral-shaped molecule inside most living cells that carries genetic instructions. It is built on a backbone of phosphorus, oxygen, and carbon atoms. In all living things, from plants and animals to microbes, these instructions tell cells which molecules to make.
extinct An adjective that describes a species for which there are no living members.
genus (plural: genera) A group of closely related species. For example, the genus Canis — which is Latin for “dog” — includes all domestic breeds of dog and their closest wild relatives, including wolves, coyotes, jackals and dingoes.
Homo A genus of species that includes modern humans (Homo sapiens). All had large brains and used tools. This genus is believed to have first evolved in Africa and over time evolved and radiated throughout the rest of the world.
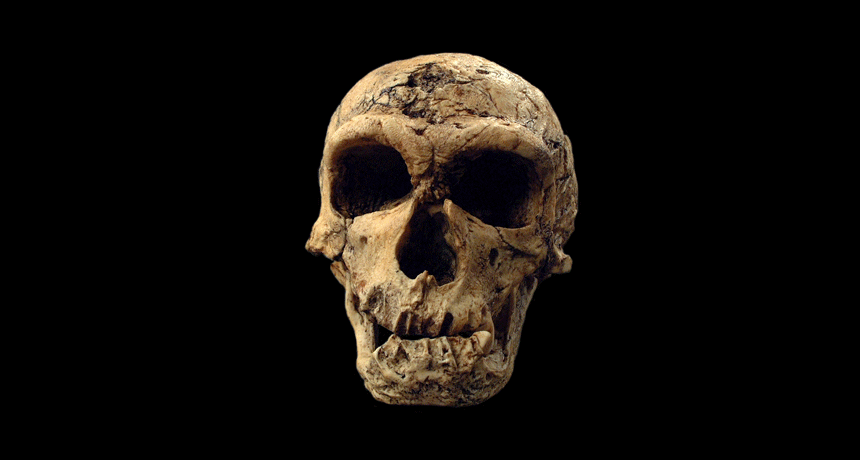
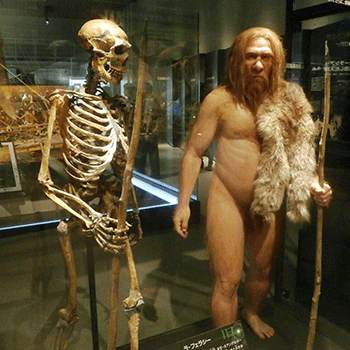
Neandertal A species (Homo neanderthalensis) that lived in Europe and parts of Asia from about 200,000 years ago to roughly 28,000 years ago.
species A group of similar organisms capable of producing offspring that can survive and reproduce.
tar A thick, viscous black flammable goo derived from coal or wood. It consists of a range of hydrocarbons, resins, alcohols and more.
tool An object that a person or other animal makes or obtains and then uses to carry out some purpose such as reaching food, defending itself or grooming.