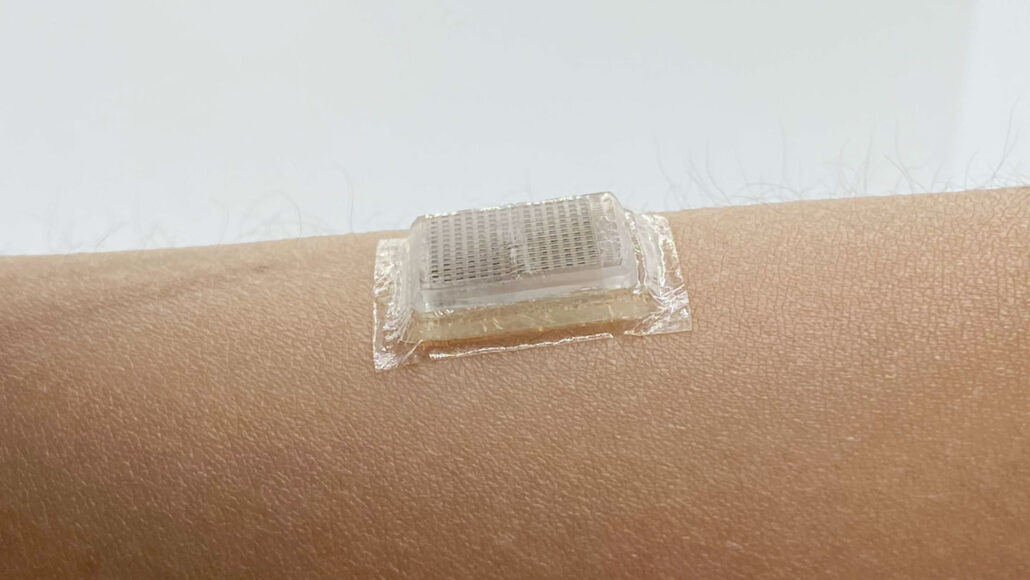
3-D: Short for three-dimensional. This term is an adjective for something that has features that can be described in three dimensions — height, width and length.
bacteria: (singular: bacterium) Single-celled organisms. These dwell nearly everywhere on Earth, from the bottom of the sea to inside other living organisms (such as plants and animals). Bacteria are one of the three domains of life on Earth.
biomedical engineer: An expert who uses science and math to find solutions to problems in biology and medicine; for example, they might create medical devices such as artificial knees.
clot: (in medicine) A collection of blood cells (platelets) and chemicals that collect in a small region, stopping the flow of blood.
COVID-19: A name given to the disease that erupted into a massive global pandemic in 2020. It first emerged in 2019 and is caused by a new coronavirus known as SARS-CoV-2. Symptoms can include pneumonia, trouble breathing, feeling too tired to walk more than a few steps, fever, headaches, low blood-oxygen levels, blood clots and brain “fog.”
develop: To emerge or to make come into being, either naturally or through human intervention, such as by manufacturing. (in biology) To grow as an organism from conception through adulthood, often undergoing changes in chemistry, size, mental maturity or sometimes even shape.
diagnose: To analyze clues or symptoms in the search for their cause. The conclusion usually results in a diagnosis — identification of the causal problem or disease.
engineer: A person who uses science to solve problems. As a verb, to engineer means to design a device, material or process that will solve some problem or unmet need. (v.) To perform these tasks, or the name for a person who performs such tasks.
heart attack: Permanent damage to the heart muscle that occurs when one or more regions of it become starved of oxygen, usually due to a temporary blockage in blood flow.
heart rate: Heart beat; the number of times per minute that the heart — a pump — contracts, moving blood throughout the body.
mechanical engineer: Someone trained in a research field that uses physics to study motion and the properties of materials to design, build and/or test devices.
organ: (in biology) Various parts of an organism that perform one or more particular functions. For instance, an ovary is an organ that makes eggs, the brain is an organ that makes sense of nerve signals and a plant’s roots are organs that take in nutrients and moisture.
smartwatch: A watch that can perform a host of functions, including search for information on the internet.
sonar: A system for the detection of objects and for measuring the depth of water. It works by emitting sound pulses and measuring how long it takes the echoes to return.
sound wave: A wave that transmits sound. Sound waves have alternating swaths of high and low pressure.
statistics: The practice or science of collecting and analyzing numerical data in large quantities and interpreting their meaning. Much of this work involves reducing errors that might be attributable to random variation. A professional who works in this field is called a statistician.
system: A network of parts that together work to achieve some function. For instance, the blood, vessels and heart are primary components of the human body's circulatory system. Similarly, trains, platforms, tracks, roadway signals and overpasses are among the potential components of a nation's railway system. System can even be applied to the processes or ideas that are part of some method or ordered set of procedures for getting a task done.
technology: The application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes, especially in industry — or the devices, processes and systems that result from those efforts.
tissue: Made of cells, it is any of the distinct types of materials that make up animals, plants or fungi. Cells within a tissue work as a unit to perform a particular function in living organisms. Different organs of the human body, for instance, often are made from many different types of tissues.
ultrasound: (adj. ultrasonic) Sounds at frequencies above the range that can be detected by the human ear. Also the name given to a medical procedure that uses ultrasound to “see” within the body.
wave: A disturbance or variation that travels through space and matter in a regular, oscillating fashion.
wireless: (in telecommunications) An adjective that describes the ability of certain devices to send and receive radio signals over the air. It often refers to Wi-Fi networks and the networks operated by cell-phone companies to transmit data called up by phone users.