Try This: Walking on water with science
To walk on water, take advantage of tension. An experiment will show you how
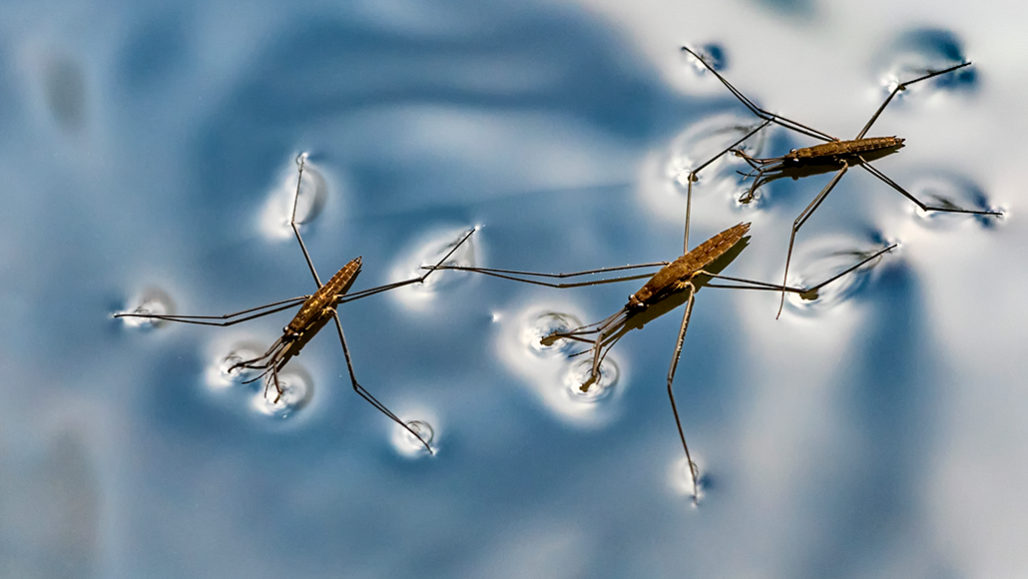

Water striders float easily on top of the water. How do they keep from sinking? An experiment can help you find out.
JanMiko/iStock/Getty Images Plus
This article is one of a series of Experiments meant to teach students about how science is done, from generating a hypothesis to designing an experiment to analyzing the results with statistics. You can repeat the steps here and compare your results — or use this as inspiration to design your own experiment.
Splash through a puddle and you get your feet wet. But little insects called water striders can skim right across the water’s surface. How do they do it? They’re very small, but that’s not it. They’re very light, but that’s not everything, either. To find out one of the key reasons water striders, er, stride, I have to come up with an experiment.
For any experiment, I need a hypothesis, or statement that I can test. But first, I need to know a little bit about water.
Spill water onto a plastic table, and it will form droplets — tiny balls of water. This happens because of surface tension. Water molecules are attracted to each other. They form weak bonds between each other. Where these molecules meet air, the exposed water molecules can’t attach to any more molecules in front of them — there’s air there. Instead, they end up attaching to the water molecules next to them, holding on even tighter. These molecules resist anything that tries to break them up. Then, a single water droplet will form with its outer layer of water molecules acting somewhat like a very thin skin that holds the droplet together — surface tension.
Water also has buoyancy. This is the upward force that a fluid exerts toward something being pressed against it. Water molecules take up space and exert pressure upward, forcing up anything that is pressing down. If there’s more pressure up from the water than there is down from an object, an object will float. If the object is exerting more pressure down, it will sink.
To walk across water, water striders could be taking advantage of surface tension and buoyancy. To take advantage of surface tension, all they need to do is not break the surface of the water molecules. To take advantage of buoyancy, the striders would have to be putting down as little pressure on the water as possible. That way, the pressure up from the water would let them float.
One way to achieve both of these goals is to spread out. A water strider has six long legs. Those legs are spread wide across the water. Maybe this increased area lets them spread their weight out. That way, each leg exerts less pressure on the water and fails to break through the surface tension. They way, the water strider floats along on the surface.
If this is how water striders manage their walking-on-water feat, then there’s something there I can test. I can find out if spreading weight over an increased area helps things to float.
Now I have a hypothesis: Objects with a larger surface area will float more often than objects of the same mass with a smaller surface area.
Wiring it up
For my experiment, I won’t use real water striders. Instead, I’ll create fake ones out of wire. I also need a tray of water and a ruler. If you try this experiment at home, you may also want a thick, heavy book. More on that in a minute.

I started with a spool of wire that is 0.25 millimeter (0.01 inch) thick. This is often called 30-gauge wire. This wire is so light that my digital scale can’t even measure it. So to make sure that my fake water striders are all the same mass, I cut the wire into pieces of the same length: 20 centimeters (7.9 inches).
To make fake water striders with larger and smaller surface areas, I formed the wire into flat circles of different diameters. How many pieces do I need? I could test two groups — small and large circles. But if some small circles float, and some large circles sink, it won’t really help me. I need to test each size many times, and I also need to test more than two sizes.
So I cut 60 lengths of wire. I tested five different circle sizes, and tested each circle size 12 times.
For a 20-cm piece of wire, the largest complete circle I could make was around 55 to 60 mm across (around 2 inches). The smallest was 18 to 20 mm across (around 0.75 inch). My middle sizes were around 30, 40 and 45 to 50 mm. Because I made them by hand, they all varied slightly. I used a big, flat book to squish each circle as flat as possible. I wanted to make sure they all had the same chance to sink or float.
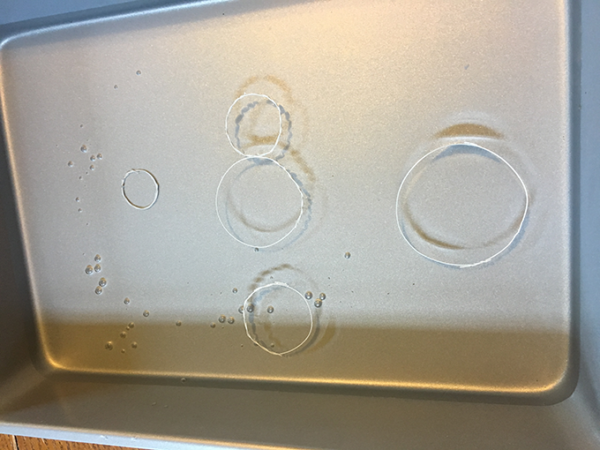

How much area do these circles contain? If you have the diameter of a circle, it’s easy to figure out. The area of a circle can be found with the formula A = π r2. π is pi, roughly equal to 3.14159. It’s the ratio, or relationship, between the circumference of a circle (how far it is around) and its diameter (how long it is across). r is the radius, which is half the diameter. In this equation, the radius is squared (or multiplied by itself).
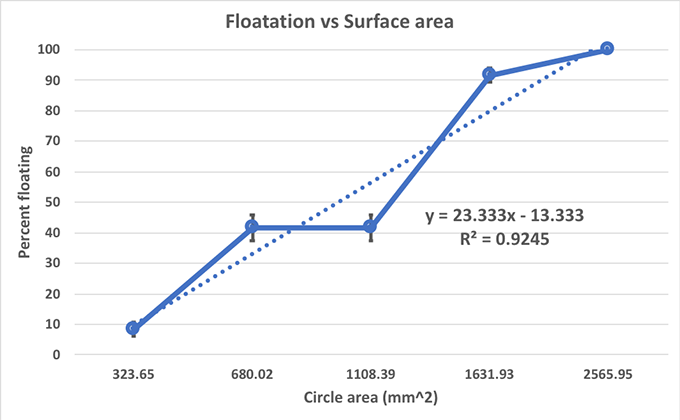
It’s easy enough to do this math yourself, but there are many free calculators online. All you have to do is plug in the radius of your circle. My largest circle has an area of around 2,565 square mm (or almost 4 square inches). My smallest has an area of around 323 square mm (0.5 square inch). The three sizes in between had areas of 680, 1,108 and 1,633 square mm (between 1.0 and 2.5 square inches)
Then, I placed each circle gently onto my tray of water. Did it sink or float? I noted which sank and which floated, for all 60 of my wire circles.
Staying afloat
I organized my data into a spreadsheet. I noted how many circles in each group sank or floated. Then I converted each number to a percentage.

For the smallest circle size, only eight percent of my circles floated (one out of 12). For the largest circle size, 100 percent of the circles bobbed neatly on the surface. As my circles increased in area, the percent that floated also increased.
What does this mean for my hypothesis? Does it mean that larger circles float more often than smaller ones? It looks like it. But I’d better have some numbers to back me up.
In this case, I’ve inserted a trendline in the graph of my data. This line shows the equation that would give me the slope of my line. It also shows me an R2 value. This is a measure of how well the size of my circles correlates with whether they sink or float. The closer an R2 value is to 1.0, the stronger the correlation — or association between size and floatation. My R2 value is 0.9245. Anything above 0.5 is accepted as a positive correlation. That means that as one variable goes up, the other one does, too. In this case, I have a positive correlation between circle size and how likely my circles are to float.
This seems to support my hypothesis. Objects with a larger surface appear more likely to float than those with a small surface area.
Next steps
No study is perfect. In this one, I divided my sizes into groups. But it might be better to have even more variability in my circle sizes. I could also try to mimic a water strider better. Water striders are light and their legs spread out in a circle. But their legs are still individual legs. Next time, I might build something a little more strider-like.
Another experiment I might try would involve breaking up the surface tension of the water. For that, I would need a surfactant — a chemical that decreases the attraction between water molecules. Luckily, surfactants aren’t hard to find. Soaps are surfactants. Would adding soap to my water make it harder for my striders to float? I’d have to do another experiment to find out.
But based on these data, it does appear that objects with a larger surface area are likely to float more often than objects with a smaller surface area. And that is, in fact, how water striders do it. They use their long legs to spread their weight on the water. Each individual leg holds very little weight. Get wide enough, and the surface tension of the water remains intact. And the water strider can keep on striding.
Note: This story has been updated to correct a metric conversion error.







