colleague: Someone who works with another; a co-worker or team member.
crustaceans: Hard-shelled water-dwelling animals including lobsters, crabs and shrimp.
filter: (n.) Something that allows some materials to pass through but not others, based on their size or some other feature. (v.) The process of screening some things out on the basis of traits such as size, density, electric charge.
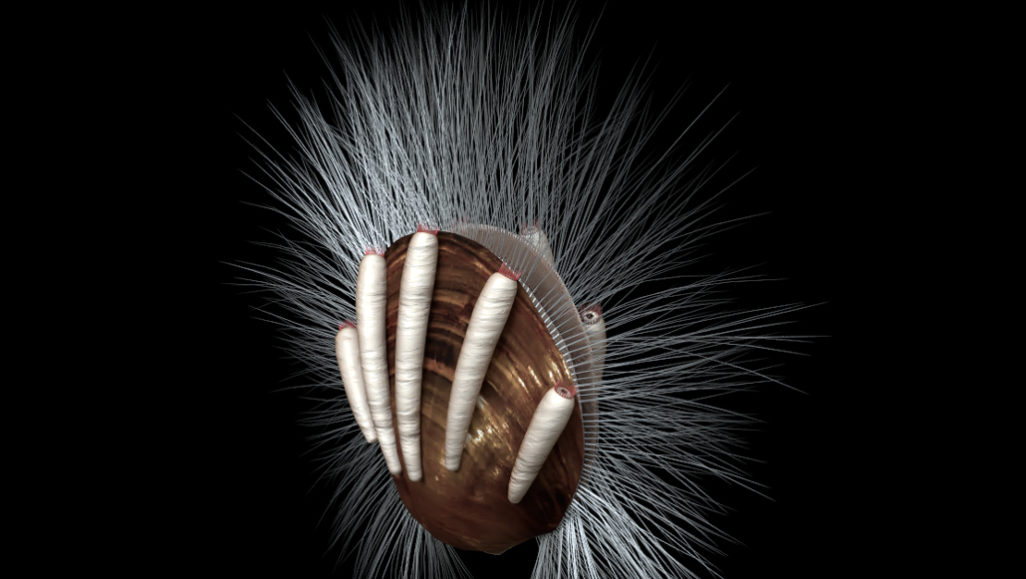
filter feeder: A water-dwelling animal that collects its nutrients or prey by filtering them out of the water. Some of the best known examples are bivalves, such as clams and mussels.
fossil: Any preserved remains or traces of ancient life. There are many different types of fossils: The bones and other body parts of dinosaurs are called “body fossils.” Things like footprints are called “trace fossils.” Even specimens of dinosaur poop are fossils. The process of forming fossils is called fossilization.
host: (in biology and medicine) The organism (or environment) in which some other thing resides. (v.) The act of providing a home or environment for something.
organism: Any living thing, from elephants and plants to bacteria and other types of single-celled life.
paleontologist: A scientist who specializes in studying fossils, the remains of ancient organisms.
parasite: An organism that gets benefits from another species, called a host, but doesn’t provide that host any benefits. Classic examples of parasites include ticks, fleas and tapeworms.
sea: An ocean (or region that is part of an ocean). Unlike lakes and streams, seawater — or ocean water — is salty.
sediment: Material (such as stones and sand) deposited by water, wind or glaciers.
shell: The protective, hard outer covering of mollusk or crustacean, such as a mussel or crab.