Using art to show the threat of climate change
These seven artists are using climate change concepts in their work

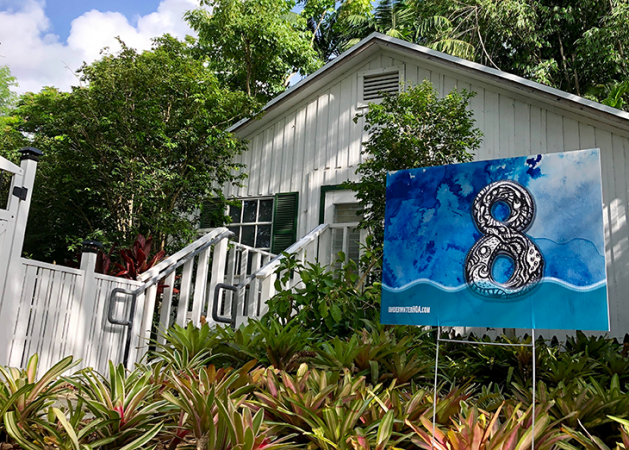
This painted sign, by Xavier Cortada, is a marker that someone can plant in their yard. It shows how high the sea would have to rise to flood the owner’s home (5 feet, or 1.5 meters).
Xavier Cortada
Climate change can be a tough topic to face. Permafrost is thawing, sea levels are rising and glaciers are melting. But in our day-to-day lives, those changes can be hard to see. Most of us don’t live near glaciers or beaches. Most of us won’t build a house on permafrost. How do we grasp the problem? Maybe we need art.
From epic operas to video games to city-spanning painted projects, here are seven artists, scientists and composers who are using art to spread the word about our changing climate.
Gaming the changing climate
EarthGamesUW/YouTube
Climate change is “one of these topics that makes people want to turn off and disengage,” says Dargan Frierson. “It shouldn’t be that way.” Frierson is a climate scientist at the University of Washington in Seattle. He created a game called Climate Quest to help players engage with climate change. Why a game? “There are so many things that games can do,” he says, that help people connect to big problems like climate change. “You can speed up time, visualize things that are invisible or … fail a few times before you’re eventually successful.”
In the game, disasters strike all over the United States. Players are given a roster of experts such as urban planners and climate scientists. Send the right expert out, solve the problem and save the day. Frierson and three colleagues pulled the simple game together in a single weekend at a hackathon — an event where people work together to build solutions to problems. “A lot of educational games are not very good because they’re a little bit boring,” he says. “It’s most important to make it fun first.”
This is what climate change sounds like
Institute on the Environment, University of Minnesota/YouTube
Scientists often state that the planet has warmed by 1 degree Celsius (1.8 degrees Fahrenheit) since 1850. But the weather from year to year varies. It’s hard to grasp just what one degree of overall warming is like.
That’s why Daniel Crawford picked up his cello.
Crawford studies climate at the University of Minnesota in St. Paul. When he was a college student, he worked with Scott St. George, a scientist who studies climate by looking at ancient tree rings. “He had been interested in using music to convey trends in climate change data,” Crawford says.
Crawford and St. George started with a dataset of surface temperatures beginning in 1880. By matching each yearly temperature change with a musical note, Crawford composed a “song for our warming planet.” As the temperature gets warmer, the notes get higher. The result is a creepy tune. “The maps, the graphs and the numbers are not conveying the message,” Crawford says. He and St. George hope that music might make a difference.
Climate change dresses up

Artist Michele Banks frequently uses science in her work. “I use science as a way to approach ideas about life in general,” she says. “I find it really fascinating … it helps us get closer to answers about big questions.” Banks is based in Washington, D.C., and usually paints with watercolor.
But when she decided to create a piece about climate change for an art show, Banks started with a wedding dress. “I called it the marriage of ice and carbon, the Arctic bride,” she says. The dress is the usual wedding white on the top. That represents the Arctic’s ice. But as the climate warms, the frosty Arctic melts. Banks’ dress dissolves into a weedy mass of green. “It doesn’t give you a feeling of growth. It’s that icky dull brown and green that you see when the snow melts,” she says. “That’s a lot of what’s up in the Arctic right now. It’s not a happy green.”
By using a wedding dress — something that everyone will know — Banks hopes that her project will bring climate change home. “I want people to think about the effects that their decisions and their ways of life are having on places that are far away from them.”
Glacial dance
Diana Movius designed a ballet performance that represents melting ice and moving glaciers.
D. Movius/Vimeo
Dancers can use their bodies to show people falling in love. They can show war and triumph, happiness and sadness. And now they can show climate change.
Diana Movius is a choreographer (kor-E-AH-grah-fur) — someone who designs dances and movements. Movius designed a dance about glaciers. The dancers perform in front of images of drifting ice. Their bodies help show how glaciers break off of ice sheets — a process called calving — and melt into the sea.
Climate change takes television
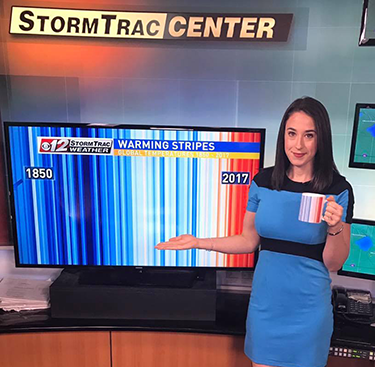
Scientists often use charts and graphs when presenting climate change data. But Ed Hawkins decided to do it with stripes. He studies climate at the University of Reading in England. He created an eye-catching array of stripes to show how the world has warmed over time, going from a cool blue to an angry red.
When Jeff Berardelli saw the pattern, he wanted to use it to show climate change to the world. Berardelli is a meteorologist who at the time was working at CBS12 in West Palm Beach, Fla. Meteorologists study weather and climate — and you might see them on television giving the weather report.
Berardelli put the pattern on ties, mugs, jewelry, shirts and buttons. And he spread the word to other meteorologists to wear the stripes on screen on the first day of summer in 2018. Lauren Olesky, another meteorologist at CBS12, grabbed a striped coffee mug. She was excited about spreading awareness of climate change. “We now understand the importance of this message,” she says. “And we all have platforms that allow us to share this vital information.”
Sing a song of climate change
This is a sound clip from the climate change opera Auksalaq.
Matthew Burtner, Scott Deal
Growing up in the tiny village of Nuiqsit, on the northern edge of Alaska, Matthew Burtner experienced climate change firsthand. “I would come home from college, and I would see the changes taking place in Alaska were dramatic,” he says. Burtner is now a composer at the University of Virginia in Charlottesville. He wrote an opera about climate change. The opera is “Auksalaq,” from the Inupiat (people native to Alaska) word for melting snow and ice.
Burtner combined recordings of scientists’ talking about climate change, interviews with people native to Alaska and opera singers in seven different places around the world. In 2012, all the groups performed together at the same time from different places, teaming up over the internet. The audience even added their own thoughts to the opera via an app. Their ideas showed up as words that opera singers added to their performance. “I’ve come to the position that music can bring something unique to these discussions,” he says.
Bringing climate change home
Some places will feel climate change impacts sooner than others. Xavier Cortada is an environmental artist living outside Miami, Fla. He knew that Miami would suffer from sea level rise. “It’s at ground zero,” he says. “The elevation is so low.” The city is so flat and close to the waterline that sea level rise is already creating floods. Cortada became frustrated that Miami was not addressing the issue. So he “created a process to make sea level rise impossible to ignore,” he says.
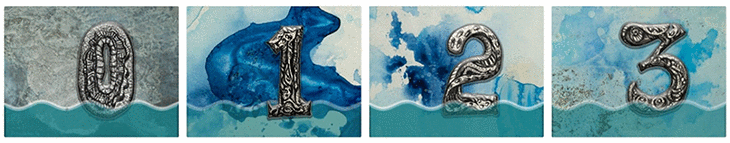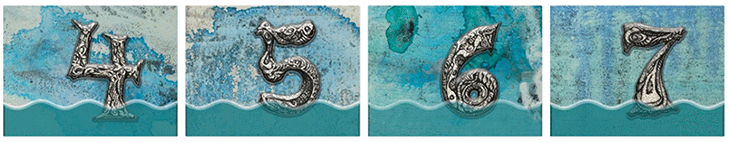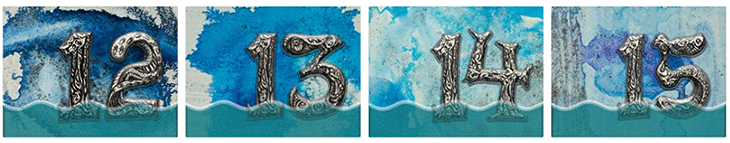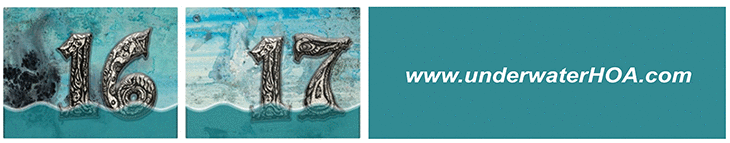
In a project called “Underwater Home Owners’ Association,” Cortada painted numbers and waterlines onto thousands of large signs. Each number corresponded to how high someone’s house or business was above sea level. A “one” would mean that if the sea level rose one foot (0.3 meter), the house would flood. Cortada gave the signs to home owners in Pinecrest, Fla., which is near Miami. The home owners put them in their yards. Kids painted more signs and put them near their schools and along busy roads.
The art project has already had a real-world effect, Cortada says. The people who put the signs in their yards created a real home owners’ association to address climate change in their communities. At their first meeting, he says, they elected an ocean scientist as their leader.








