Is weather control a dream or nightmare?
People are changing the weather, and that may not be good

Weather control is the stuff of science fiction, but scientists have made it at least a little bit real. Whether people should be controlling their weather, though, is another matter.
Nastco/iStockphoto
Wildfires burned through thousands of acres of forest and darkened the skies over Oregon and Washington for weeks. A drought destroyed crops in Montana and the Dakotas. Hurricanes brought torrential rains and flooding to Florida and Puerto Rico. Homes, businesses — and lives — were lost.
These events are but a sampling of the destruction that a bad turn in the weather can cause. And they occurred in just one month this year — September — in just the United States.
It’s no wonder that people have long sought to control the weather. The right amount of sun and rain brings healthy crops, safety and prosperity. Too much or too little — starvation and death.
In fiction, people can alter the weather. The X-Men’s Storm, for instance, uses her control of the atmosphere to create tornadoes, blizzards, lightning and other phenomena. A witch named Jadis brings never-ending winter to the land of Narnia in The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe. And the new movie Geostorm has a modern take, with an array of weather-controlling satellites that keep the planet’s destructive forces in check.
None of this is possible in reality. No one can deter a hurricane with gunfire (despite rumors to the contrary). No one can tame a tornado with liquid nitrogen (although someone has obtained a patent for the concept). Still, people are changing the weather.
Weather modification, of a sort, has been possible since the 1940s. We can now cause some clouds to dump extra moisture on demand. People also have begun to transform the weather in an unintentional way — through activities that have been altering Earth’s climate. There even is debate over whether programs should be developed to undo such changes with geoengineering.
The big question, though, is whether changing Earth’s weather is a good idea at all.
Seeding clouds
It’s January, about 80 kilometers (50 miles) north of Boise, Idaho. Two planes take off and fly into the clouds. On the ground are mobile radar stations that for weeks will be snowed in place. Atmospheric scientists control all of this equipment, waiting for an experiment to start. They are part of a project called SNOWIE. That’s short for Seeded and Natural Orographic Wintertime Clouds — the Idaho Experiment. (Orographic refers to something that is related to mountains.) The scientists here are studying cloud seeding, a method that aims to boost how much rain or snow falls from the sky.

Cloud seeding got its start in 1946. That’s when chemist Vincent Schaefer was experimenting with a cloud in his laboratory.
He wanted to chill the cloud, so he put dry ice — frozen carbon dioxide — into the chamber. Instantly, the chamber was full of ice crystals. “Dry ice, falling on the cloud, caused submicroscopic bits of ice to appear in the cloud,” Science News reported in January 1947. This “turned to snow and fell earthward.”
Later research replaced the dry ice with tiny particles of silver iodide.
To get this into a cloud, scientists first mix the compound with a flammable material. That material is then burned, sending smoke filled with silver iodide particles up into the cloud.
Those particles become nuclei that can allow liquid water raindrops to freeze and become ice crystals. High in a cloud, water vapor will condense around these newly formed ice crystals, causing them to grow. When the crystals get big enough, they fall to the ground. This is similar to what naturally happens in a cloud that will go on to produce precipitation. Dust, smoke or salt can all become nuclei that naturally allow a cloud’s liquid drops to freeze.
Once cloud seeding was discovered, scientists started wildly speculating about what might be on the horizon. An end to hail. Filled drinking-water reservoirs. Prevention of deadly ice storms. Changing the path of tornadoes.
“Even one of the scientists that … won the [1932] Nobel Prize said in 10 years we can change the course of a hurricane,” recalls Roelof Bruintjes. He’s an atmospheric scientist at the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in Boulder, Colo. In fact, he notes, “Subsequent research has shown us things are much more complex than that.” Cloud seeding might work, but not for every cloud in every place.

In the 1950s and 1960s, the United States and other governments invested heavily in weather-modification research. They saw potential not only for helping their people but also for aiding the military. Weather control could be a potential weapon. It also could let armies guarantee they got the weather they needed for a particular operation.
However, what worked well in the lab didn’t quite pan out in the skies. Not every attempt at cloud seeding ended with rain or snow. And even in those that did, it was impossible to tell if the seeding caused that precipitation or if the rain or snow would have fallen on its own. “There’s a lot of natural variability,” explains Jeffrey French. He’s an atmospheric scientist at the University of Wyoming in Laramie.
In time, money for cloud-seeding research dwindled. More effort was put into improving weather prediction. Weather modification did not, however, disappear. More than 50 nations now have cloud-seeding programs, according to the World Meteorological Organization. China, for instance, set off hundreds of rockets to seed clouds in 2008. Its goal was to ensure clear skies for the opening ceremonies of the summer Olympics in Beijing. There also are dozens of private weather-modification companies. And many other companies pay for cloud seeding.
What they achieve, today, is much more subtle than the grand visions that had once been proposed. “Under certain conditions, [cloud seeding] can probably be quite effective,” says French. It might produce some 15 percent more precipitation during a storm, he estimates. But just what the right conditions still are not completely known.
A snowy winter
That’s where SNOWIE comes in. Idaho Power, an electric company, had been running a cloud-seeding program for years. It wanted more winter snow in the nearby area’s mountain snowpack. When that snowpack melts in spring and summer, it feeds rivers and lakes. It also runs Idaho Power’s hydroelectric dams. Without enough water, the company can’t provide enough energy to its consumers. Cloud seeding makes sense for this company. But those efforts need better data if they are to really pay off.
Unlike in a lot of scientific fields, it’s difficult to set up controlled experiments in atmospheric science, notes French. “We are stuck with the laboratory of the sky and experiments that are never ever 100-percent repeatable, because every time you go out and make measurements, things are different. So we look for situations in where we can try to do somewhat controlled experiments. And cloud seeding, it turns out, is one of those areas.”

In their experiment, SNOWIE scientists would seed a portion of a cloud from one aircraft. Then they would use the second aircraft to take measurements within that cloud — both where it had been seeded and where it had not. The part without seeding was the control (unchanged) condition for the experiment.
The researchers collected a variety of data. These include the range of cloud-particle sizes and cloud temperatures, which could be as cold as –10° Celsius (14° Fahrenheit). They took high-resolution images of the cloud crystals. This would show them something about how the crystals grew. Radar on the aircraft and on the ground provided data about the broader cloud structure. This might tell them where the precipitation was, the depth of the cloud and the height of the cloud’s top.
“All of those things are important when one looks at the processes that are occurring in the cloud,” explains French. “When you consider cloud seeding, we’re really only trying to modify one or two processes.”
The team’s evaluation of all those data is still to come. The results will aid in future cloud seeding in Idaho. They also will help scientists understand the natural traits of clouds and what goes on within them. “If we can’t understand those,” French says, “we have no hope in understanding the impacts of the cloud seeding itself.”
Changing the world’s weather
Meanwhile, human activities have begun changing the weather — and in some less-than-subtle ways. Through climate change, says Bruintjes of NCAR, “We are already modifying the weather.”
Kevin Petty is a meteorologist and the chief scientific officer for Vaisala, in Louisville, Colo. This company provides weather-related observations and software to governments and other groups to help with decision-making. Weather and climate are different beasts, but they are related, he notes. “Weather is what’s happening over a very short period of time, whereas climate is what happens, on average, over a longer period.”
One of the best ways that Petty has seen this summed up is: Climate is what you expect; weather is what you get. A region’s climate might dictate that on average a summer day is sunny and 30 °C (86 °F). But on any particular summer day, the weather might be 35 °C (95 °F) with thunderstorms.
The planet’s climate and weather patterns are changing because human activities have increased the amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Those gases act like a big blanket covering Earth. They help to keep heat in. Without those gases, Earth would be a giant ice ball. But as those gases increase, it’s as if the blanket is getting thicker and thicker, holding in more heat.
The planet is now holding in more heat than it has for thousands of years. That extra heat provides more energy for the processes that drive the planet’s weather. And those effects are wide-ranging.
Story continues below image.
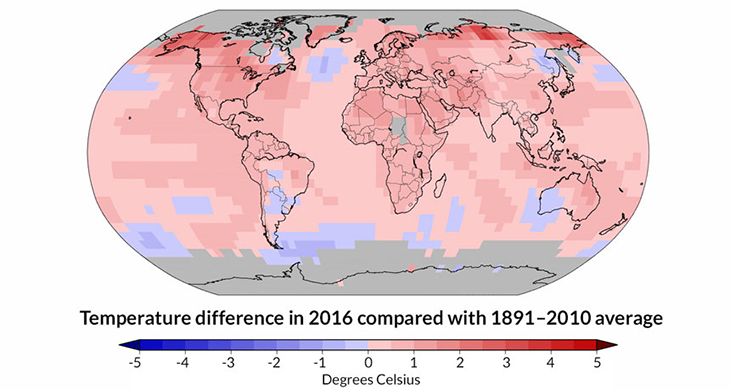
Average temperatures on the planet have been increasing, notes David Titley. He’s an atmospheric scientist at Pennsylvania State University in University Park. He headed up a task force on climate change when he was a rear admiral in the U.S. Navy. What was considered a hot day in the 1960s tends to be several degrees cooler than it is now. Likewise, today’s winter days aren’t quite as cold as they once were. No surprise, Earth has been setting regular records for average temperature, with 2016, 2015 and 2014 being the hottest on record.
And that’s just the start.

“Warm air holds more water vapor,” Titley notes. “When it rains, it can rain more intensely.” That makes floods more likely. Warmer air also causes more water to evaporate from the soil. “So you can get drought conditions more quickly,” he explains. “Drought begets drought.” Once a drought begins, it can self-perpetuate, making the lack of precipitation more prolonged.
Scientists are still looking into how climate change might affect other types of extreme weather, such as hurricanes and tornadoes. And it’s likely that there is some kind of effect, such as hurricanes becoming more intense. The heavy rains and particularly strong winds in the recent spate of hurricanes that struck the United States in 2017 — Harvey, Irma and Maria — were probably due in part to climate change.
These changes to weather patterns ripple across the planet. They cause problems from the minor to the extreme. “You’ll still be able to go skiing in the Rockies,” Titley says, but in places like Washington, D.C., a snowy Christmas will become even less likely than it is now.
Worse effects will be — and have been — felt elsewhere in the world. Syria is a nation in the Middle East where a civil war has been raging for years. That conflict was sparked in part by a bad drought. Titley notes that people who are already well off probably won’t suffer as much from climate change. “If you’re one of the other … billions of people in the world, it can be life threatening.”
Story continues below image.

Is manipulating climate a good idea?
There is no “magic bullet” for undoing the damage caused by climate change, Titley says. “The best way to reduce the impact of climate change is to adapt to the effects of a changing climate … and to transition to non-carbon-based sources of energy to stop putting greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.” (Non-carbon sources? He means energy sources such as hydroelectric, solar and wind power, and possibly nuclear power.) But scientists also have proposed two methods of climate intervention, or geoengineering.
One idea is to somehow suck excess carbon dioxide (CO2) out of the atmosphere. That will not be easy. The gas is causing problems, yes, but there’s actually not a whole lot of it, on a percentage basis. There are just 400 or so molecules of CO2 for every million molecules of air. “Imagine going into a playhouse with a million white balls and there are 400 red ones,” Titley says. Finding those 400 red balls would be difficult. On a global scale, there are many, many molecules of CO2. It would be very expensive to find and selectively remove them. And then they would have to be stored somewhere — forever.
Another type of intervention would dim the sun. Or rather, it would reflect into space some of the sunlight before it reaches the ground. “If we turn down the sun … then we don’t have as much heat coming in and therefore we won’t warm up,” Titley explains. “We think this can be done.”
Tiny particles called aerosols would have to be pumped high into the atmosphere (higher than where jet planes fly). There, they would reflect some of the sun’s energy, preventing it from reaching the ground.
This is similar to what happens naturally after a huge volcanic explosion that spews particles high into the air. Those effects only last for a few years. Then the particles fall out. So if aerosol seeding were to be done on purpose, those aerosols would have to be pumped into the atmosphere continuously.
This would require a lot of money and nonstop commitment. It also would do nothing to stop one big aspect of climate change: ocean acidification. (When carbon dioxide dissolves in water, it makes the water more acidic. That would be true whether sunlight was being blocked or not.)
And light filtering might change rainfall in ways that aren’t predictable today. “So, you may cool the planet,” Titley says. But, he adds, “You may also stop all the rains coming to India and South China, where about two [billion] to three billion people depend on those rains for their basic food crops.”
Those unintended consequences get to why tinkering with the climate in any way might be a bad idea. Petty would caution strongly against any type of deliberate manipulation of weather or climate. “If you do this in one part of the world,” he asks, what might occur elsewhere?
Basic properties of the planet drive Earth’s weather, notes Bruintjes. These include the steady flow of energy from the sun, the rotation of the Earth and the release of water vapor from the oceans. “If we change those, then we might not be living anymore,” he worries. He doesn’t think cloud seeding would cause a problem. But Petty and some others are not so sure. They’re leery about even something as small as that.
In the movie Geostorm, someone hijacks the system for controlling the weather. Satellites that had kept the planet safe have now been turned into weapons that create tsunamis, tornadoes and deadly hail storms. It’s all fake, but it does offer a lesson for real life. Like the movie’s tagline says, “Some things were never meant to be controlled.” And that probably includes Earth’s weather.
UNAVCO, Inc.