Why are bird eggs in cold climates darker colored?
A global survey suggests that it might help keep them warmer
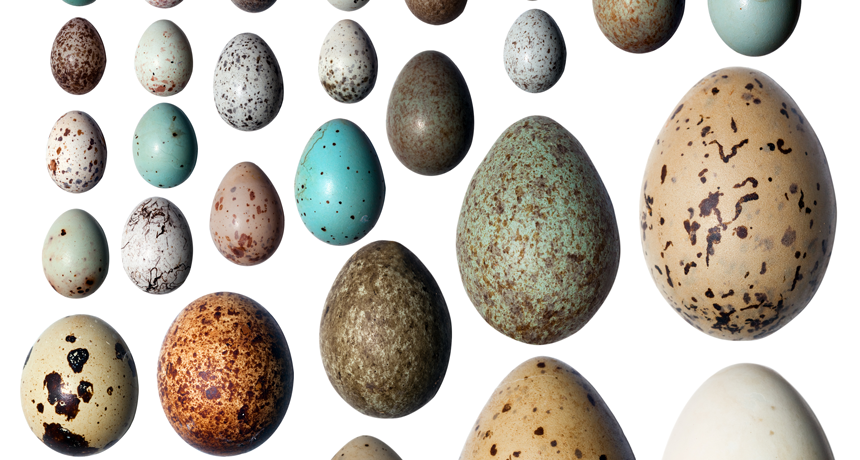

Bird eggs come in a wide variety of shapes, sizes and colors. A new study finds that northern birds in colder climates tend to have darker eggs.
Ornitolog82/iStock/Getty Images Plus
Bird eggs come in a dizzying array of colors. But from a global perspective, that diversity follows a simple pattern, new research shows. The colder the climate, the darker the egg.
Darker eggs absorb more heat than lighter ones. This could help developing chicks stay warm while their parents forage for food. That’s the conclusion of the study. It appeared online October 28 in Nature Ecology and Evolution.
Biologists have long tried to understand why birds’ eggs come in so many shapes and colors. There could be many reasons. Color may help camouflage eggs from predators. Egg shape or color might also somehow protect eggs against bacteria or signal their quality. Shape or color might even help keep an egg warm. Scientists have turned up some evidence to support all of these hypotheses, says Phillip Wisocki. He worked on the research while studying biology at Long Island University Post in Brookville, N.Y.
Adds Daniel Hanley, scientists were never sure whether any of these factors were important to egg diversity. This biologist advised Wisocki on his research.
Hanley, Wisocki and their colleagues turned to collections of birds’ eggs in museums. They compiled data from 634 species. These represented all but four of the 40 living orders of birds. Then they plotted the data on a global map. The brightness and color of eggshells closely correlated with a region’s temperature, they showed. That was true even after considering that closely related species can have similarly colored eggs.
Birds in “the far north — which tends to be colder — had darker, browner eggs,” Hanley says. Eggs became lighter and slightly bluer for birds closer to the equator. Egg colors, however, tended to be more varied in the tropics.
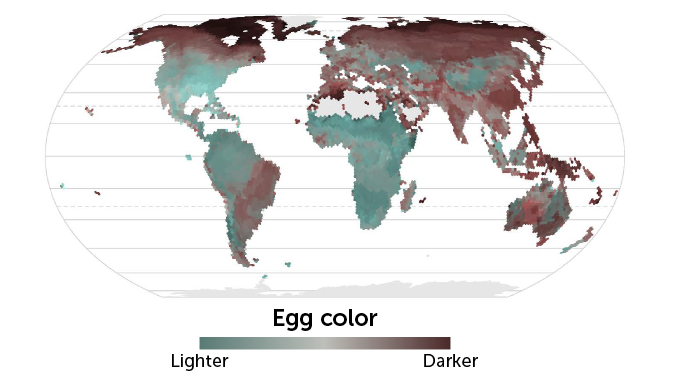
Darker eggs may be an adaptation to the cold, the researches now suggest. Like a dark car parked in the sun, a dark egg should absorb more heat from the sun than a lighter egg. To test this theory, Hanley’s group exposed chicken eggs to direct sunlight and tracked how well they retained heat. Some were white. Others were brown or blue. Sure enough, brown eggs warmed faster and cooled more slowly than the lighter eggs.
“In the Arctic, parents have to go out to forage and get back to their eggs quickly,” Hanley says. “If you can buy them five extra minutes, that can actually be really beneficial.”
Mary Caswell Stoddard is a biologist at Princeton University in New Jersey. She welcomed the study’s attention to the role of color in regulating an egg’s warmth. “That’s part of what makes this study — and the discovery that birds living in colder habitats tend to lay darker eggs — so exciting,” she says. However, other factors will play a role, too, she notes.
Still, Wisocki says the study shows climate to be a major driver in egg colors. It also expands the notion of what color is for. “We usually think about color through the lens of perception,” he says. It might play a role in mating displays, camouflage or signaling. But here, he says, “We show that color matters, but the observer isn’t important.”







