evolutionary biologist: Someone who studies the adaptive processes that have led to the diversity of life on Earth. These scientists can study many different subjects, including the microbiology and genetics of living organisms, how species change to adapt, and the fossil record (to assess how various ancient species are related to each other and to modern-day relatives).
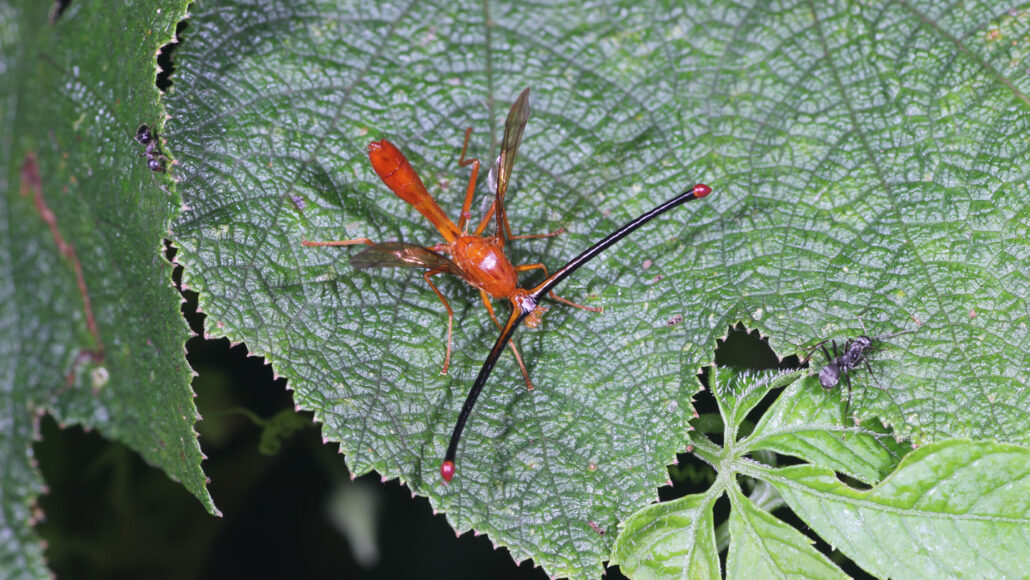
insect: A type of arthropod that as an adult will have six segmented legs and three body parts: a head, thorax and abdomen. There are hundreds of thousands of insects, which include bees, beetles, flies and moths.
morph: Short for metamorphose, it means to change or transform from one form to another (such as from a caterpillar to a butterfly) or from one shape to another. Or it can mean to evolve or mutate, where one or more parts of the genome undergo some sort of change in their chemistry — and potentially in their function.
sequence: The precise order of related things within some series.
sex: An animal’s biological status with respect to reproductive functions, typically male or female. There are a number of indicators of biological sex, including sex chromosomes, gonads, internal reproductive organs, and external genitals.
species: A group of similar organisms capable of producing offspring that can survive and reproduce.