
Bethany Brookshire was a longtime staff writer at Science News Explores and is the author of the book Pests: How Humans Create Animal Villains. She has a B.S. in biology and a B.A. in philosophy from The College of William and Mary, and a Ph.D. in physiology and pharmacology from Wake Forest University School of Medicine. She was a 2019-2020 Knight Science Journalism Fellow at MIT, the winner of the Society for Neuroscience Next Generation Award and the Three Quarks Daily Science Writing Award, among others.

All Stories by Bethany Brookshire
-

More classroom time increases reading skills
Keeping kids in school for a few extra hours could mean better reading comprehension — no matter how the teachers use the time. But those extra hours come with extra cost.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentScientists Say: Plastisphere
As plastic floats in the ocean, it can acquire its own colony of microbes and algae. We call this ecosystem the plastisphere.
-

Teen makes sure bacteria stay hands-off
Germs are everywhere. One teen has designed a way to keep them from sticking to a surgeon’s gloves.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Toxin
It is safe to refer to any poison as toxic. But while all toxins are poisonous, most poisons are not toxins.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Cyanide
Cyanides are poisonous. But they are more than that. This group of compounds is used in everything from mining to capturing fish.
-

Ink leads way to terminating termites
Inspired by a classroom experiment, a teen has built a way to lure troublesome termites to their death — using the power of ink.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentTeens use science to worm through plastic waste
Some beetle larvae can eat plastic, which might be good for our pollution problem. But which types eat the most can vary a lot, these young scientists find.
-
 Space
SpaceScientists Say: Wormhole
Scientists have predicted the presence of tunnels in space that connect two points in space and time. They are named for the shape they resemble.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentFighting big farm pollution with a tiny plant
Fertilizer runoff can fuel the growth of toxic algae nearby lakes. A teen decided to harness a tiny plant to sop up that fertilizer.
-
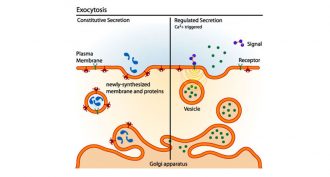 Life
LifeScientists Say: Exocytosis
For a cell to remove something large from inside itself, it turns to a process called exocytosis.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Acidification
When a solution becomes more acidic, it’s acidifying. And that’s not always a good thing.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEating toxic algae makes plankton speedy swimmers
After slurping up harmful algae, copepods swim fast and straight — making them easy prey for hungry predators.