
Laura Sanders reports on neuroscience for Science News. She wrote Growth Curve, a blog about the science of raising kids, from 2013 to 2019 and continues to write about child development and parenting from time to time. She earned her Ph.D. in molecular biology from the University of Southern California in Los Angeles, where she studied the nerve cells that compel a fruit fly to perform a dazzling mating dance. Convinced that she was missing some exciting science somewhere, Laura turned her eye toward writing about brains in all shapes and forms. She holds undergraduate degrees in creative writing and biology from Vanderbilt University in Nashville, where she was a National Merit Scholar. Growth Curve, her 2012 series on consciousness and her 2013 article on the dearth of psychiatric drugs have received awards recognizing editorial excellence.

All Stories by Laura Sanders
-
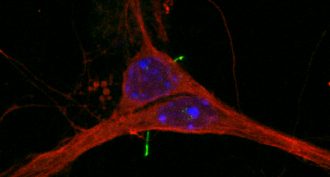 Brain
BrainTeeny tiny hairs on brain cells could have big jobs
Brain cells have tiny antennae called cilia. But no one really seemed to know what they did. Now, scientists have shown they could play a role in obesity.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDog wins tally of nerve cells in the outer wrinkles of the brain
Golden retrievers rate at the top for numbers of nerve cells, a study of some carnivores finds.
-
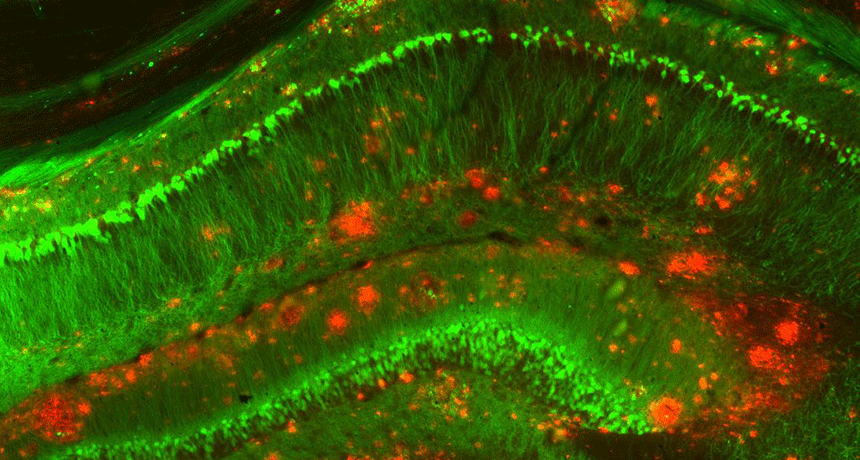 Brain
BrainAlzheimer’s protein can sneak into the brain from the blood
Experiments in mice show that proteins linked with Alzheimer’s disease can enter the brain from the blood, then stockpile there.
-
 Brain
BrainBrains may need flexible networks to learn well
New data suggest that brain cells may learn best when they are able to easily make and break off communications with neighbors — or distant brain regions.
-
 Brain
BrainTo reveal how the brain creates joy, start by tickling rats
Rats love a good tickle. Not only do they beg for more, but the action itself activates a part of the brain that detects touch, researchers find.
-
 Brain
BrainLying sets up a liar’s brain to lie more
As people lie more, activity in one brain region falls, a new study finds. It’s an area associated with emotion.
-
 Brain
BrainPain is contagious — at least in mice
Pain can move from one mouse to another. The trigger may be smell.
-
 Brain
BrainOut-of-whack body clock causes more than sleepiness
When the body’s “clock” doesn’t match the cues its getting from outside, people can feel bad. Researchers are using math to explain this “circadian-time sickness.”
-
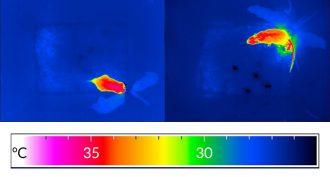 Brain
BrainMice brains hint at how bodies keep their cool
Nerve cells in mice can keep the body cool and may prevent high fevers. The discovery could have implications for obesity and other health issues.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTo remember something new: Exercise!
People who exercised strenuously for a half hour after learning something new cemented those memories. But the trick: Wait four hours before getting the heart pumping vigorously.
-
 Brain
BrainLeft brain stands guard during sleepovers
Part of the left half of the brain remains on alert while the rest of the brain and body snooze.
-
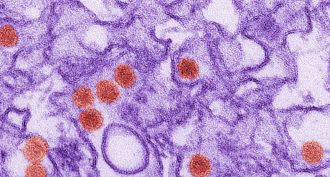 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists link Zika to nerve disease
The Zika virus is spreading in the Americas. There has also been an uptick in cases of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Scientists think the two are linked.