
Sid Perkins
Freelance Writer
Sid is a freelance science journalist. He lives in Crossville, Tenn., with his wife, two dogs and three cats. He specializes in earth sciences and paleontology but often tackles topics such as astronomy, planetary science, materials science and engineering.
In 2009, Sid won the Award for Distinguished Science Journalism in the Atmospheric and Related Sciences from the American Meteorological Society. And in 2002, he shared the American Astronomical Society’s Solar Physics Division’s Award for Popular Writing on Solar Physics. Sid’s writing also appears in Science, Nature, Scientific American, the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences and Science News.

All Stories by Sid Perkins
-
 Fossils
FossilsNew fossils bring the wide world of pterosaurs to life
The latest clues from fossils hint at where these flying reptiles came from, how they evolved, what they ate and more.
-
 Earth
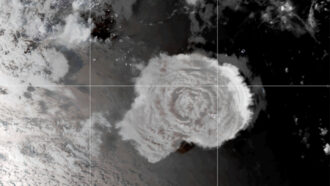
EarthOne 2022 tsunami may have been as tall as the Statue of Liberty
A massive volcanic eruption in the South Pacific, earlier this year, appears to have triggered one tsunami that was initially 90 meters (nearly 300 feet) tall.
-
 Space
SpaceBehold: The biggest known comet in our solar system
This “dirty snowball” in space is about twice as wide as Rhode Island and darker than coal.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe end of the dinosaurs appears to have come in springtime
Fish fossils from North Dakota suggest when the Chicxulub asteroid devastated Earth, triggering the mass extinction of dinosaurs and other species.
-
 Fossils
FossilsDinos may have had the sniffles 150 million years ago
A respiratory infection that spread to air sacs in the vertebrae of a sauropod dinosaur likely led to the dino's now-fossilized bone lesions.
-
 Fossils
Fossils‘Penis worms’ could have been the original hermits
These soft-bodied critters lived in abandoned shells about 500 million years ago, a new study suggests.
-
 Planets
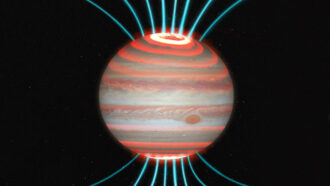
PlanetsJupiter’s intense auroras heat up its atmosphere
Jupiter’s hotter-than-expected upper atmosphere may be warmed by charged particles slamming into the air above the poles.
-
 Oceans
OceansMoon’s orbital wobble can add to sea-level rise and flooding
In a dozen years or so, the tide-enhancing effects of a wobble in the moon’s orbit should lead to dramatically higher sea levels in some coastal cities.
-
 Tech
TechSynthetic trees could tap underground water in arid areas
They also could also help coastal residents mine fresh water from salty sources.
-
 Tech
TechHeadphones or earmuffs could replace needles in some disease testing
A new system that uses earmuffs to collect gases coming out the skin could help doctors diagnose a variety of diseases, scientists say.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEngineers surprised by the power of an elephant’s trunk
An elephant's trunk can suck air through it fast — at more than 335 miles per hour (150 meters per second)!
-
 Animals
AnimalsCommon parasite may help mussels survive heat waves
By whitening shells, the organism helps the shellfish stay cool on sunny days, a new study suggests.