Biological Evolution: Unity and Diversity

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWhat we can — and can’t — learn from our pets’ DNA
Your dog or cat’s DNA is an open book. DNA tests tell people about their pet’s breed and attempt to predict things about its behavior and health.
-
 Earth
EarthExplainer: Understanding geologic time
Geologic time is unimaginably long. Geologists puzzle it out using a calendar called the Geologic Time Scale.
By Beth Geiger -
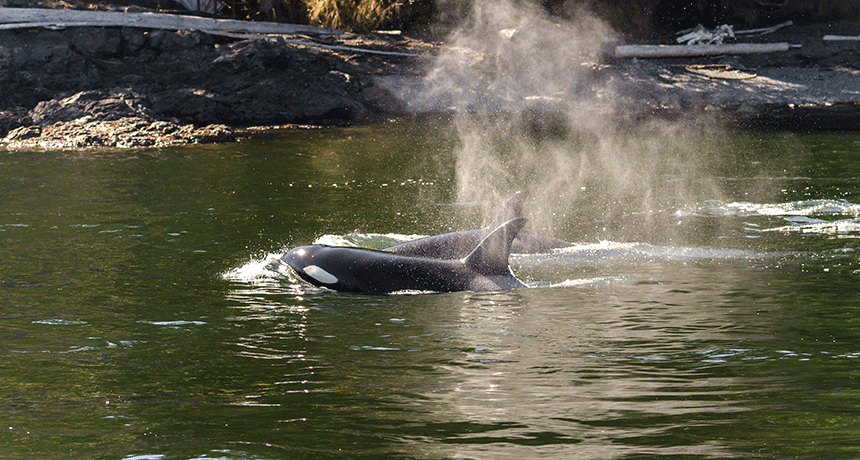 Animals
AnimalsOrca snot leads to a whale of a science-fair project
DNA found in the mucus of orcas suggests that even though the traits of family pods may differ, these marine mammals all appear to belong to a single species.
By Sid Perkins -
 Chemistry
ChemistryCool Jobs: Diving for new medicines
Scientists mix research with underwater adventure as they search the oceans for new chemicals to treat infections, cancer and more.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsExplainer: Why scientists sometimes ‘knock out’ genes
How do we learn what a particular molecule does in the body? To find out, scientists often 'knock out' the gene that makes it. Here’s how.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What is a hormone?
Various tissues secrete special chemicals, known as hormones. They travel, usually in blood, to a particular distant site where they tell certain cells it’s time to go to work.
By Janet Raloff -
 Genetics
GeneticsExplainer: How CRISPR works
Scientists are using a tool called CRISPR to edit DNA in all types of cells.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA tells tale of how cats conquered the world
Ancient DNA study suggests that domesticated cats spread across the ancient world in two waves.
-
 Archaeology
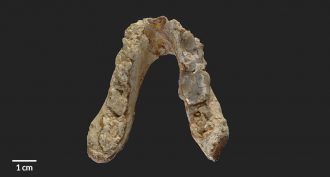
ArchaeologyEuropean fossils may belong to earliest known hominid
New fossils suggest that the earliest non-ape human ancestors may have evolved in Europe, not Africa.
By Bruce Bower -
 Fossils
FossilsStudy claims to have found oldest human fossils
Humans, as a species, may be much older than previously thought. They also may have evolved further North and West of the suspected cradle of human evolution.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsHow the house mouse found its home
Once people started settling down 15,000 years ago, a mouse species followed them indoors. The animals didn’t need people to be farming and storing food.
-
 Life
LifeWeird mega-worm found to have odd diet
Giant shipworms have bacteria in their gills that produce food for them. This has made their digestive organs shrink from lack of use.