Earth's Place in the Universe
-
 Space
SpaceSpacecraft traveling through a wormhole could send messages home
A probe going through a wormhole should be able to send messages home before such a tunnel forever closes, a new computer model finds.
-
 Math
MathScientists Say: Calculus
Calculus is math that deals with curves, from their changing slopes to the areas they enclose.
-
 Planets
PlanetsSaturn’s moon Enceladus wears a thick blanket of snow
Pits on the frosty moon reveal the snow’s surprising depth, up to 700 meters (2,300 feet) in some places.
-
 Planets
PlanetsThe dwarf planet Quaoar hosts an impossible ring
Quaoar’s ring lies outside the Roche limit. That’s an imaginary line beyond which rings aren’t thought to be stable.
-
 Physics
PhysicsLet’s learn about the quantum realm
On the smallest scales, the universe behaves in some pretty strange ways.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Fission
Nuclear fission is the process of splitting atoms apart to release huge amounts of energy.
-
 Physics
PhysicsExplainer: Radioactive dating helps solve mysteries
Knowing the decay rate of radioactive elements can help date ancient fossils and other artifacts.
By Trisha Muro -
 Earth
EarthFossil-fuel use is confusing some carbon-dating measurements
Carbon-14 dating of recent artifacts will soon give scientists confusing results. That’s another price society pays for its reliance on fossil fuels.
By Trisha Muro -
 Space
SpaceNASA is readying to send humans back to the moon
The launch of NASA's Artemis I is a huge step toward sending humans back to the moon and beyond.
By Liz Kruesi -
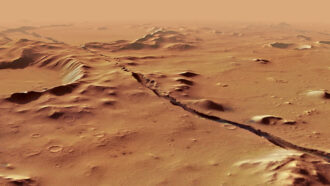 Planets
PlanetsMars might still be volcanically active, quakes there suggest
Seismic rumblings picked up by NASA’s InSight lander hint at molten rock moving deep below the planet’s fractured surface.
-
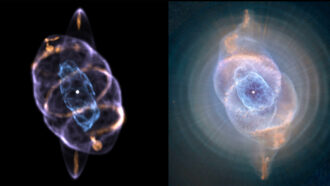 Space
SpaceJets may have sculpted rings of Cat’s Eye nebula
The Cat’s Eye nebula is one of the most complex of its kind. A 3-D model now reveals the source of that complexity.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Neutron
Neutrons are one of the main building blocks of atoms and have no electric charge.