Earth's Place in the Universe

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Space
SpaceHere’s an easier new way to weigh a black hole
The timing of flickers in the gas and dust of a black hole’s accretion disk correlates to its mass, a new study finds.
-
 Earth
EarthLet’s learn about meteor showers
Meteor showers happen when Earth’s orbit passes through trails of debris left behind by comets or asteroids.
-
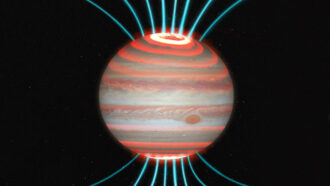 Planets
PlanetsJupiter’s intense auroras heat up its atmosphere
Jupiter’s hotter-than-expected upper atmosphere may be warmed by charged particles slamming into the air above the poles.
By Sid Perkins -
 Earth
EarthScientists Say: Anthropocene
Humans are changing the world in profound ways. Some scientists think those changes have launched a new epoch in Earth’s history: the Anthropocene.
-
 Oceans
OceansMoon’s orbital wobble can add to sea-level rise and flooding
In a dozen years or so, the tide-enhancing effects of a wobble in the moon’s orbit should lead to dramatically higher sea levels in some coastal cities.
By Sid Perkins -
 Space
SpaceLet’s learn about dark matter
Dark matter is only detectable by the gravitational pull it exerts on visible objects, like stars and galaxies.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Plasma
In physics, plasma refers to one of the four states of matter. In medicine, plasma describes the part of blood that ferries cells, nutrients and more throughout the body.
-
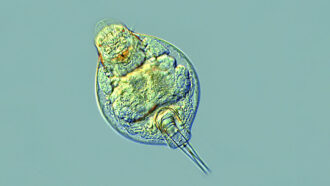 Animals
AnimalsTiny animals survive 24,000 years in suspended animation
Tiny bdelloid rotifers awake from a 24,000-year slumber when freed from the Arctic permafrost.
-
 Space
SpaceThis image may be the first look at exomoons in the making
These observations offer some of the best evidence yet that planets around other stars have moons, or exomoons.
-
 Climate
ClimateNew UN climate report finds no time for denial or delay
It links extreme weather around the globe to Earth’s changing climate.
-
 Space
SpaceBorn in deep shadows? That could explain Jupiter’s strange makeup
Dust that blocked sunlight might have caused the gas giant to form in a deep freeze, a new study suggests.
By Ken Croswell -
 Space
SpaceCosmic filaments may have the biggest spin in outer space
These rotating threads of dark matter and galaxies stretch millions of light-years. Scientists want to know how their spin begins.