Earth's Systems
-
 Environment
EnvironmentGas stoves can spew lots of pollution, even when they’re turned off
A new study finds they can leak benzene and other harmful chemicals into homes, sometimes at very high levels.
By Laura Allen -
 Earth
EarthAnalyze This: Salt may quash lightning over the sea
Bits of airborne salt may help raindrops form, removing water from clouds before it can freeze as part of the process that makes lightning.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHow salty does the sea have to be for an egg to float?
Some objects float on top of the ocean, and other objects sink to the bottom. Why? Try this eggs-periment to find out!
-
 Climate
ClimateExplainer: What is decarbonization?
Lowering carbon levels in our atmosphere to stabilize the climate may start with switching from fossil fuels to greener energy sources.
By Laura Allen -
 Physics
PhysicsExplainer: What is friction?
The force of friction always acts to slow things down. It depends on just two factors: the surfaces and how hard they press together.
By Trisha Muro -
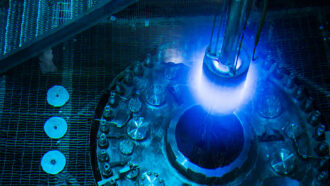 Physics
PhysicsExplainer: Radiation and radioactive decay
Like clockwork, radioactive forms of some elements shed parts of themselves as they attempt to become nonradioactive.
By Janet Raloff and Trisha Muro -
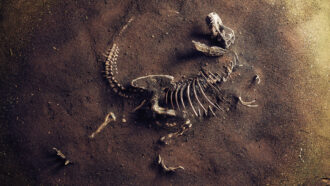 Physics
PhysicsExplainer: Radioactive dating helps solve mysteries
Knowing the decay rate of radioactive elements can help date ancient fossils and other artifacts.
By Trisha Muro -
 Earth
EarthFossil-fuel use is confusing some carbon-dating measurements
Carbon-14 dating of recent artifacts will soon give scientists confusing results. That’s another price society pays for its reliance on fossil fuels.
By Trisha Muro -
 Climate
ClimateGreenland’s inland ice is melting far faster than anyone thought
Inland melting of the Northeast Greenland Ice Stream is accelerating — and may contribute far more to sea level rise than earlier estimates suggested.
By Nikk Ogasa -

-
 Earth
EarthAnalyze This: Wildfires are pumping more pollution into U.S. skies
Researchers wanted to study the health effects of wildfire smoke. But they realized they didn’t know where it was and how much exposure people had.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Neutron
Neutrons are one of the main building blocks of atoms and have no electric charge.