Earth's Systems
-
 Physics
PhysicsCosmic timeline: What’s happened since the Big Bang
Energy, mass and the cosmos' structure evolved a lot over the past 13.82 billion years — much of it within just the first second.
By Trisha Muro -

-
 Earth
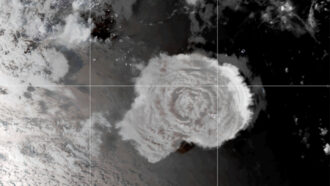
EarthOne 2022 tsunami may have been as tall as the Statue of Liberty
A massive volcanic eruption in the South Pacific, earlier this year, appears to have triggered one tsunami that was initially 90 meters (nearly 300 feet) tall.
By Sid Perkins -
 Climate
ClimateHeat waves appear more life-threatening than scientists once thought
This is bad news as a warming planet leads to growing numbers of excessive heat waves — and millions more people facing potentially deadly temperatures.
-
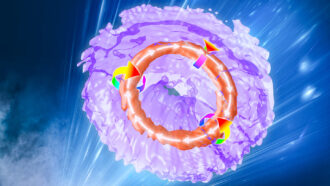 Physics
PhysicsScientists used lasers to make ‘smoke rings’ of light
Physicists had a bright idea: Make light into swirling, ring-shaped vortices, similar to smoke rings or bubble rings.
-
 Earth
EarthUplifting Antarctic shores point to accelerating loss of glaciers
It appears the Pine Island and “Doomsday” Thwaites glaciers are losing ice — and shrinking faster — than at any time in the past 5,500 years.
By Douglas Fox -
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceLet’s learn about diamond
Diamond is born under extreme heat and pressure inside Earth and elsewhere in the universe.
-
 Earth
EarthScientists Say: Fault
A fault is a crack in Earth’s crust where pieces of rock scrape past each other.
-
 Earth
EarthTiny gemstones show when Earth’s crust first started moving
Chemical hints observed in zircons suggest when the important process of plate tectonics first took off.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Space
SpaceGravitational waves ‘kicked’ a newborn black hole across space
Two black holes merged into one, and then sped off at around 5 million kilometers (3.1 million miles) per hour.
-
 Earth
EarthScientists Say: Atmosphere
An atmosphere is an envelope of gas around a planet, dwarf planet or moon.
-
 Tech
TechThis sun-powered system delivers energy as it pulls water from the air
The device not only produces electricity but also harvests water for drinking or crops. It could be especially useful in remote and dry parts of the world.
By Laura Allen