Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics
-
 Plants
PlantsBefore eating, Venus flytraps must ‘count’
Researchers find that Venus flytraps respond to the number of times insects touch their sensory hairs. This tells them when it’s time to turn on digestion.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineZika virus raises alarm as it spreads in the Americas
Zika virus has been in Africa and Asia for decades. But is has now spread to the Americas. And it may cause a devastating birth defect.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe truth about zits
A common bacterium called P. acnes usually helps keep the skin healthy. But under some conditions, and especially during puberty, it can trigger painful, embarrassing outbreaks of unsightly pimples.
-
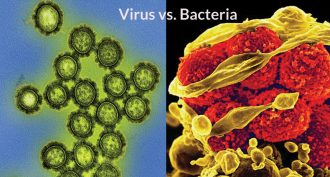 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBehavior of genes could identify type of infection
The behavior of hundreds of genes can identify a viral infection, a new study finds. That could help doctors determine treatment for a sick patient.
-
 Plants
PlantsBanana threat: Attack of the clones
Researchers find that disease-causing fungi — all clones of one another — will continue to infect banana plants unless new steps are taken to stop their spread.
-
 Climate
ClimateConcerns about Earth’s fever
Burning fossil fuels is causing the planet to heat up, causing weather patterns to change, sea levels to rise and diseases to spread.
-
 Animals
AnimalsProfile: A human touch for animals
Temple Grandin uses her own autism to understand how animals think. The animal scientist is famous for fostering the humane treatment of livestock.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentWildlife forensics turns to eDNA
Environmental DNA, or eDNA, tells biologists what species have been around — even when they’re out of sight or have temporarily moved on.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsTaking attendance with eDNA
Environmental DNA, or eDNA, tells biologists what species are in an area — even when they’re out of sight.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistrySome air pollutants seep through skin
The skin is the body’s largest organ. And it can let in as much or more of certain air pollutants than enter through the lungs, a new study finds.
By Janet Raloff -
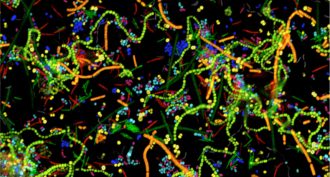 Microbes
MicrobesSlime cities
Biofilms are like tiny cities of bacteria — some harmless, others destructive. Scientists are learning how to keep these microscopic metropolises under control.
-
 Fossils
FossilsClues to the Great Dying
Millions of years ago, nearly all life on Earth vanished. Scientists are now starting to figure out what happened.
By Beth Geiger