From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceLet’s learn about microplastics
Microplastics have turned up everywhere from the highest mountains to the bottom of the ocean — and even inside animals and people.
-
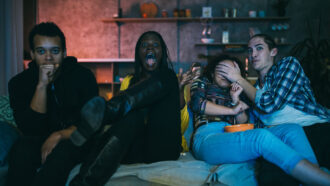 Science & Society
Science & SocietyWhat’s the fun in fear? Science explores the appeal of scary movies
On its face, the appeal of horror doesn’t make much sense. But scientists are starting to uncover who’s most likely to enjoy scary films and why.
-
 Plants
PlantsScientists Say: Fruit
Some foods usually called vegetables — such as tomatoes, cucumbers and peppers — are actually fruits.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSea creatures’ fishy scent protects them from deep-sea high pressures
TMAO’s water-wrangling ability protects a critter’s critical proteins — including muscle — from crushing under deep ocean pressures.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis acrobatic spider flips for its food — literally
An acrobatic hunting trick lets the Australian ant-slayer spider catch prey twice its size, a new study shows.
By Freda Kreier -
 Health & Medicine
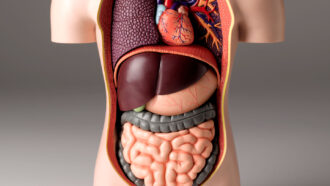
Health & MedicineScientists Say: Liver
This organ in the upper-right side of the belly does many essential jobs, such as cleaning blood and producing bile.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow sunshine may make boys feel hungrier
Males eat more on long summer days, but females do not. Hormones may explain this difference.
-
 Chemistry
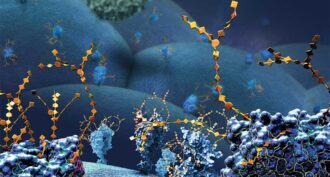
ChemistryLego-like way to snap molecules together wins 2022 chemistry Nobel
This so-called ‘click chemistry’ allows scientists to build complex molecules in the lab and in living cells.
By Meghan Rosen and Nikk Ogasa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExamining Neandertal and Denisovan DNA wins a 2022 Nobel Prize
Svante Pääbo figured out how to examine the genetic material from these hominid ‘cousins’ of modern humans.
By Tina Hesman Saey and Aimee Cunningham -
 Animals
AnimalsLiving mysteries: This critter has 38 times more DNA than you do
The genomes of salamanders are bloated with genetic “parasites.” That extra DNA slows down their lives and strands them in perpetual childhood.
By Douglas Fox -
 Life
LifeScientists Say: Fungi
Although some fungi can cause diseases, others can be eaten, used to make medicines or serve other useful functions.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow boa constrictors squeeze their prey without strangling themselves
Tracking boas’ ribs in X-ray videos revealed the snakes’ squeezing secrets. It’s the latest Wild Things cartoon from Science News Explores.
By Maria Temming and JoAnna Wendel