From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
-
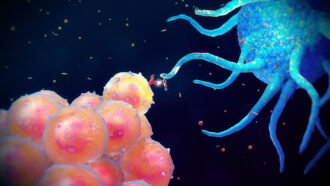 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: The body’s immune system
An army of cells — and their protein arsenal — work to keep us safe. Several squads of special forces possess unique superpowers to disable or kill intruders.
-
 Life
LifeScientists Say: Cellulose
Cellulose is an abundant natural polymer found in plants and algae. It’s used to make everything from paper to clothing.
-
 Life
LifeExplainer: What is an endangered species?
Threats such as climate change and habitat loss can put species at risk of going extinct. Different words describe that risk.
-
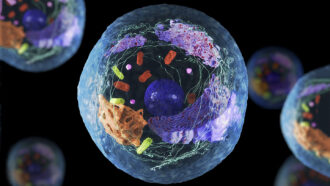 Life
LifeExplainer: Cells and their parts
Life as we know it depends on the coordination of structures inside cells — whether a living thing has only a single cell or trillions of them.
-
 Animals
AnimalsLa nutria soporta el frío, sin un cuerpo grande ni capa de grasa
Al mamífero más pequeño del mar no le es fácil mantenerse caliente. Ahora, los científicos han descubierto cómo sus células responden al desafío.
-
 Fossils
FossilsDinos may have had the sniffles 150 million years ago
A respiratory infection that spread to air sacs in the vertebrae of a sauropod dinosaur likely led to the dino's now-fossilized bone lesions.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsA new drug mix helps frogs regrow amputated legs
The treatment helped frogs grow working limbs useful for swimming, standing and kicking. It’ll be a while before people can do that.
-
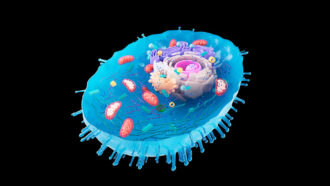 Life
LifeScientists Say: Eukaryote
Eukaryotes are living things whose cells package their genetic material inside a pouch called a nucleus.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSee the world through a jumping spider’s eyes — and other senses
Scientists are teasing out the many ways the spiders’ vision, listening and taste senses differ from ours
By Betsy Mason -
 Psychology
PsychologyAddiction can develop when reward-seeking changes a teen’s brain
Over time, the pleasure disappears and craving grows. That craving causes stress that can drive people to use drugs or pursue unhealthy behaviors again and again.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryExplainer: What are fats?
A fat molecule's three long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms repel water, stash energy and keep living things warm — even in the bitter cold.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA in air can help ID unseen animals nearby
Analyzing these genetic residues in air offers a new way to study animals. It could give scientists a chance to monitor rare or hard to find animals.
By Laura Allen