From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Computing
ComputingVirtual wounds: Computers probe healing
To better understand how the body heals wounds, scientists have begun creating computer programs that let virtual cells fight it out. These ‘computer games’ could lead to better medicines.
-
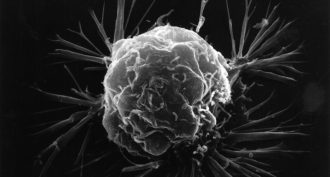 Life
LifeCell gangs may help cancer spread
A new study on mice suggests that when cancer cells strike out from a primary (first) tumor in groups, they have an especially good chance of creating new tumors elsewhere.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists say: Inflammation
When cells are injured, they send out distress signals. The rescuing cells cause more blood to flow to the area, producing inflammation.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureLivestock: A need to save rare breeds
New studies and ongoing work highlight why society should save rare livestock breeds — and the part that technology can play.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureExplainer: What is a gene bank?
Most banks store money. But some very special ones store deposits that may prove even more valuable: tissues that could prevent the extinction of breeds and species.
-
 Brain
BrainHarry Potter reveals secrets of the brain
Figuring out how the brain makes sense of what we read isn’t easy. So scientists enlisted the magical world of Harry Potter. It allowed experts to predict with great accuracy which brain areas would be active in a given part of the story.
-
 Animals
AnimalsScientists say: Hibernaculum
This week’s word is hibernaculum, the word scientists use to describe the place where an animal goes to hibernate.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentNano air pollutants strike a blow to the brain
Most people think that air pollution poses the biggest risk to our lungs. In fact, pollution hits the brain too, sometimes by traveling a direct route — through our noses. These tiny pollutants can harm IQ and more.
-
 Brain
BrainScents may affect how appealing tobacco is
Menthol’s effects on the brain may make tobacco more addicting. In contrast, foul odors might help smokers quit. Two new studies show how.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentThirdhand smoke poses lingering danger
The pollutants in cigarette smoke can linger indoors for hours. Indeed, they may pose risks long after any visible smoke is gone.
By Beth Mole -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe secret of fast runners: symmetry
Science had shown that animals and people with symmetrical bodies tend to be stronger and healthier. Now researchers find they can predict the best sprinters by measuring the top runners’ knees.
By Ilima Loomis -
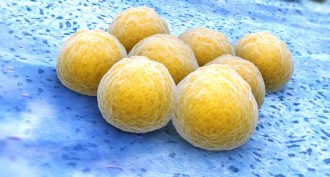 Microbes
MicrobesGerms help each other fend off antibiotics
Drug-resistant bacteria can cause persistent infections. A new study finds these germs fight drugs in different ways. And they can swap various compounds, increasing their neighbors’ chances of overcoming the drugs meant to kill them.