HS-ESS1-6
Apply scientific reasoning and evidence from ancient Earth materials, meteorites, and other planetary surfaces to construct an account of Earth's formation and early history.
-
 Planets
PlanetsMercury’s surface may be studded with diamonds
Billions of years of meteorite impacts may have transformed much of Mercury's graphite crust into precious gemstones.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Planets
PlanetsLet’s learn about Pluto
Once known as a pipsqueak planet, Pluto is now the solar system’s best known dwarf planet.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe end of the dinosaurs appears to have come in springtime
Fish fossils from North Dakota suggest when the Chicxulub asteroid devastated Earth, triggering the mass extinction of dinosaurs and other species.
By Sid Perkins -
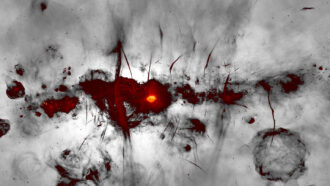 Space
SpaceWild art? No, it’s a radio image of the heart of our Milky Way
Eyelash-like radio filaments accent the brightest feature in this image — a supermassive black hole.
-
 Planets
PlanetsNo, organic molecules alone don’t point to life on Mars
These carbon-based molecules, found in a meteorite, may reflect merely a mixing of water and minerals on the Red Planet over billions of years.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Space
SpaceThe long-awaited James Webb Space Telescope has a big to-do list
The James Webb Space Telescope has been in the works for so long that new fields of science have emerged for it to study.
-
 Space
SpaceExplainer: Telescopes see light — and sometimes ancient history
Different kinds of telescopes on Earth and in space help us to see all wavelengths of light. Some can even peer billions of years back in time.
By Trisha Muro -
 Animals
AnimalsExplainer: The age of dinosaurs
Take a trip back to the Mesozoic Era to explore how geologic events, ecosystems and evolution were connected during the so-called age of dinosaurs.
By Beth Geiger -
 Planets
PlanetsNASA’s Perseverance rover grabbed its first Martian rocks
Two finger-sized pieces of stone drilled from a basalt rock are the first bits of Mars ready to be brought to Earth.
-
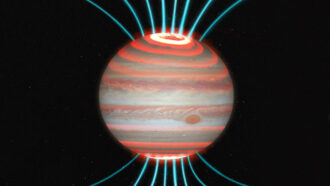 Planets
PlanetsJupiter’s intense auroras heat up its atmosphere
Jupiter’s hotter-than-expected upper atmosphere may be warmed by charged particles slamming into the air above the poles.
By Sid Perkins -
 Earth
EarthScientists Say: Anthropocene
Humans are changing the world in profound ways. Some scientists think those changes have launched a new epoch in Earth’s history: the Anthropocene.
-
 Space
SpaceLet’s learn about dark matter
Dark matter is only detectable by the gravitational pull it exerts on visible objects, like stars and galaxies.