HS-ESS2-4
Use a model to describe how variations in the flow of energy into and out of Earth systems result in changes in climate.
-
 Earth
EarthOxygen-rich air emerged super early, new data show
Scientists had thought animals were slow to emerge because they would have needed oxygen-rich air to breathe. A new study finds that plentiful oxygen may have developed early. So animals may have been late on the scene for another reason.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryParticles in air help fatten clouds’ water droplets
Making their own clouds has shown scientists how the fattest water droplets form. Understanding this could lead to better forecasts of climate change.
-
 Climate
ClimateConcerns about Earth’s fever
Burning fossil fuels is causing the planet to heat up, causing weather patterns to change, sea levels to rise and diseases to spread.
-
 Climate
ClimateExplainer: How scientists know Earth is warming
Scientists can calculate global temperatures, both present and past. Their findings show that the planet is rapidly heating up.
-
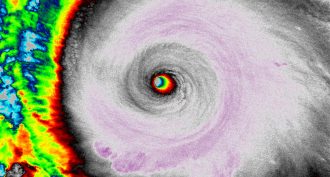 Climate
ClimatePicture This: Biggest hurricane in the West
The hurricane that’s storming into western Mexico has had higher sustained winds than any seen in the Western Hemisphere. It’s also got the lowest atmospheric pressure, making it a monster storm.
By Janet Raloff -
 Climate
ClimateNew El Niño coming on strong
The current El Niño event could be a record breaker, changing weather patterns worldwide and bringing rain to drought-parched California.
-
 Climate
ClimateWarming’s role in extreme weather
Extremes in temperature and precipitation will be more common as global temperatures rise. Human-led climate change is largely to blame, a new study finds.
By Beth Mole -
 Climate
ClimateCosmic rays offer clues about lightning
Space particles called cosmic rays pelt Earth. Scientists are using the rain of these particles to probe how lightning forms.
By Andrew Grant -
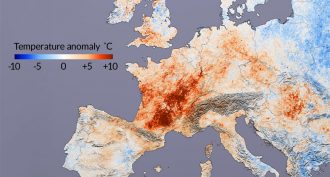 Environment
EnvironmentArctic warming bolsters summer heat
Rapid warming in the Arctic is sapping summer storms of their power to cool. That worsens heat waves across the Northern Hemisphere.
-
 Climate
ClimateScientists confirm ‘greenhouse’ effect of human’s CO2
Government scientists link directly, for the first time, a boost in warming at Earth’s surface to increasing levels of carbon dioxide. Much of that gas has been released by human activities, such as coal burning and gas-burning vehicles.
-
 Climate
ClimateLightning strikes will surge with climate change
Warming temperatures will lead to 50 percent more lightning strikes across the 48 U.S. states in the next century, researchers report. That increase could lead to more warming, more fires and even more deaths.
-
 Climate
ClimateExplainer: Why a tornado forms
Tornadoes start with a thunderstorm. But they also require other ingredients, such as instability.