HS-ESS2-5
Plan and conduct an investigation of the properties of water and its effects on Earth materials and surface processes.
-
 Earth
EarthExplainer: How is water cleaned up for drinking
Unless you’re drinking well water, city folks typically get drinking water that has been treated in a water-treatment plant. Here’s what that means.
-
 Physics
PhysicsExplainer: Winds and where they come from
Temperature and pressure are critical factors affecting why the wind blows where it does. Understanding the nature of wind can teach us a lot about weather.
-
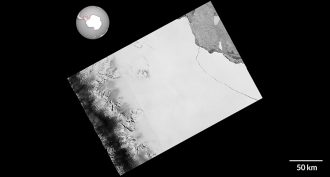 Earth
EarthAntarctic ice shelf sheds Delaware-sized iceberg
Larsen C is a major ice shelf in Antarctica. An iceberg the size of Delaware has just splintered off of it in one of the largest calving events ever recorded.
-
 Tech
TechTeen’s invention can warn of deadly rip currents
A teen lifeguard from Australia has invented a buoy that can alert swimmers to the strong, swift and deadly rip currents that can sweep them dangerously far offshore.
By Sid Perkins -
 Environment
EnvironmentArctic Sea could be ice-free by 2050
Everyone contributes to the melting of Arctic sea ice, and all are in danger of making summer ice disappear there completely by 2050, a new study finds.
-
 Climate
ClimateCool Jobs: Wet and wild weather
How’s the weather? Forecasts rely on scientists and engineers who collect and interpret data gathered on the ground, in the sky and way up in space.
-
 Earth
EarthScientists Say: Hoodoo
When softer rocks are covered with a harder rock layer, weathering can wear away the softer stone. This will leave behind tall thin towers — hoodoos.
-
 Tech
TechConcrete science
Teen researchers are exploring ways to strengthen this building material, use it for safety purposes and use its discarded rubble.
By Sid Perkins -
 Earth
EarthCarbon dioxide could explain how geysers spout
A new study overturns 150 years of thinking about Yellowstone’s geysers. Carbon dioxide, not just hot water, may be driving those spectacular eruptions.
-
 Oceans
OceansArctic ice travels fast, carrying pollution
Climate change is melting old sea ice in the Arctic. Now, younger, thinner ice is migrating far and fast, taking pollutants with it.
-
 Oceans
OceansExplainer: What is a tsunami?
Earthquakes and landslides can create huge waves that travel across oceans.
-
 Physics
PhysicsBracing sand sculptures with gravity
Natural sculptures of sandstone withstand strong winds and rains. The reason, a new study concludes: Gravity holds the sand grains together.