HS-LS1-2
Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What is puberty?
Puberty isn’t just a time for zits, breasts and deeper voices. It also spurs brain development that helps teens handle emotions and deal with stress.
-
 Brain
BrainYou don’t see as much color as you think
It might seem like we live in a world full of color. But when scientists flip it into black and white, most people never notice the switch.
-
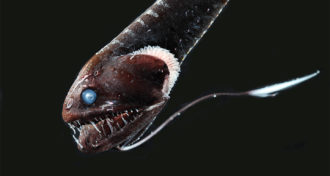 Animals
AnimalsSuperblack fish can disappear in the deep sea’s darkness
Some fish that live in the ocean’s depths are superblack due to a special layer of light-absorbing structures in their skin.
-
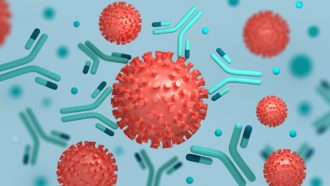 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What are Antibodies?
Antibodies are one of the major players in the immune system’s attack against germs. Learn what they are, what they do and how they keep us healthy.
-
 Brain
BrainExplainer: How our eyes make sense of light
It takes a lot for images before the eyes to be 'seen.' It starts by special cells sensing the light, then signals relaying those data to the brain.
-
 Oceans
OceansGoing bright may help corals recover from bleaching
When some corals bleach, they turn neon colors. Flashy hues may be part of a response that helps these corals recover and reunite with their algae.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryThis tube worm’s glowing slime may help sustain its own shine
Snot oozed by a marine tube worm can glow for up to 3 full days. The secret of how this works might lead to long-lasting lights that glow on and on.
-
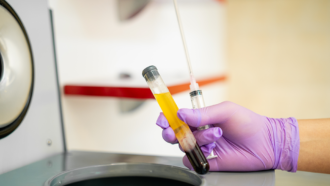 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAntibodies from former COVID-19 patients could become a medicine
The experimental treatment uses antibodies from the blood plasma of COVID-19 survivors. It may prevent disease in other people or help treat the sick.
-
 Animals
AnimalsConservation is going to the dogs
Scientists are now training dogs to help track rare, elusive — and sometimes invasive — plants and animals.
-
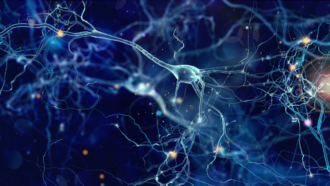 Brain
BrainZapping the brain may make it work right again
Sending electrical zaps to electrodes implanted deep in the brain can help people with Parkinson’s disease, depression and even obsessive-compulsive disorder.
-
 Life
LifeHere’s how butterfly wings keep cool in the sun
Butterfly wings sport structures that let living tissues release more heat than the rest of the wing.
-
 Animals
AnimalsOuch! Jellyfish snot can hurt people who never touch the animal
A goo shed by at least one species of upside-down jellyfish contains stinging cells. They can cause pain even to creatures that never touch the jelly.