HS-LS2-2
Use mathematical representations to support and revise explanations based on evidence about factors affecting biodiversity and populations in ecosystems of different scales.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFinding out why birds are out of range
Sometimes people see large numbers of birds outside of their normal range. A student examined how to predict these excursions.
-
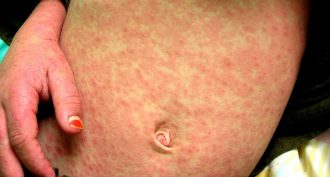 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine10 things to know about measles
Many people think that the measles vaccine wiped out the disease — at least in the United States. It hasn’t. And people who were never vaccinated face the primary risk of getting this very serious disease
-
 Animals
AnimalsHellbenders need help!
Hellbenders already face threats such as habitat loss, pollution and disease. But climate change could make matters worse. And the problems facing hellbenders could spell trouble for more than just these giant amphibians.
-
 Plants
PlantsDesert plants: The ultimate survivors
Creosote, mesquite and other desert plants rely on different adaptations to thrive, even when no rain falls for an entire year.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentImmunity: Environment can have big impact
A study on twins suggests that environmental factors can shape a person's immune system more than genes do.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsScientists say: Biomagnify
Chemicals in the environment can build up in an animal’s tissues. Predators who feed on these animals can accumulate more and more of the pollutants, a process known as biomagnification.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureLivestock: A need to save rare breeds
New studies and ongoing work highlight why society should save rare livestock breeds — and the part that technology can play.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentSpidey sense: Eight-legged pollution monitors
Spiders that prey on aquatic insects can serve as sentinels that naturally monitor banned chemicals that still pollute many rivers across the United States.
By Beth Mole -
 Microbes
MicrobesVirus blamed in starfish die-off
A virus may explains the deaths of millions of starfish along the Pacific Coast of North America. The deaths affect 20 species. Some of the stricken animals appear to melt into puddles of slime.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTiny — but mighty — food-cleanup crews
Discarded food wastes can turn city spaces into food courts for disease-carrying rats and pigeons. But a new study shows tiny cleanup crews — especially pavement ants — are doing their best to eliminate such wastes. This, in turn, makes cities less attractive to bigger pests.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesHow ‘bugs’ in our bellies impact our health
Gut bacteria can play a powerful role in human health, new studies show. In one, bacteria turned a nutrient in red meat into a chemical that boosts the risk of a heart attack. Another study shows that our genes play a role in whether we are fat or thin, probably by affecting which bacteria prefer to live in our intestines.
-
 Climate
ClimateThe worst drought in 1,000 years
The 1934 drought, during a period in American history known as the Dust Bowl, was the worst in a millennium, a new study finds. While the drought had natural origins, human activities made it worse.
By Beth Geiger