HS-LS2-2
Use mathematical representations to support and revise explanations based on evidence about factors affecting biodiversity and populations in ecosystems of different scales.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNew frog discovered in New York City
This animal could almost be mistaken for the southern leopard frog — until it opens its mouth. The call the males issue has proven unique.
By Janet Raloff -
 Animals
AnimalsComing: The sixth mass extinction?
Species are dying off at such a rapid rate — faster than at any other time in human existence — that many resources on which we depend may disappear.
-
 Animals
AnimalsRare as a rhino
Most species are rare. Some have always been rare. A problem develops when people are responsible for accelerating a species’ rarity to the point that extinction threatens.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesRecycling the dead
When things die, nature breaks them down through a process we know as rot. Without it, none of us would be here. Now, scientists are trying to better understand it so that they can use rot — preserving its role in feeding all living things.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEbola emerges in the Congo
The Democratic Republic of Congo (formerly Zaire) is where the Ebola virus was first discovered in 1976. This nation has just been hit again by the disease. Scientists suspect this is a new and independent outbreak — not a spread of the epidemic ravaging West Africa.
By Janet Raloff -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEbola treatments and vaccines could be near
Using experimental medicines against Ebola might help to slow or end an outbreak in Africa that has defied efforts to control it.
By Nathan Seppa -
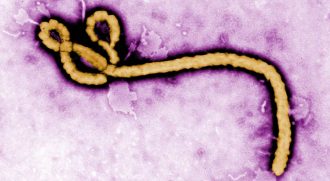 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What is Ebola?
A virus is behind the hemorrhage-inducing infection called Ebola. It causes fevers and often intense bleeding — seemingly from anywhere and everywhere.
By Janet Raloff -
 Animals
AnimalsHow termites ‘hear‘ about trouble
When danger comes too close, termites bang their heads against the walls of their homes. This action sends out a warning vibration that others ‘hear’ with their legs.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineClay: A new way to fight germs?
Geologists have discovered a type of volcanic clay that shows promise in fighting infections — maybe even ones resistant to antibiotic medicines.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentBug-killer linked to decline in birds
One of the most popular chemicals used to protect crops from bugs may also take a toll on birds, a Dutch study finds. U.S. farmers also rely on these insecticides, a second study finds.
By Stephen Ornes and Janet Raloff -
 Animals
AnimalsKeep the lights on for National Moth Week
Helping scientists is as easy as leaving your porch light on. Photograph the moths you see and upload them to the Internet for science.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesThe war on superbugs
Doctors and scientists are exploring ways to stem the growing global crisis of antibacterial resistance.