HS-LS2-2
Use mathematical representations to support and revise explanations based on evidence about factors affecting biodiversity and populations in ecosystems of different scales.
-
 Animals
AnimalsExplainer: How invasive species ratted out the tuatara
The introduction of rats to New Zealand led to huge population losses of the ancient tuatara. These uncommon reptiles vanished from the mainland. This left isolated populations to survive on several dozen isolated islands.
-
 Animals
AnimalsKangaroos have ‘green’ farts
The farts and belches of these animals contain less methane than do those from other big grass grazers. Microbes in their digestive tract appear to explain the ‘roos lower production of this greenhouse gas, a new study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsQuieter vibes for city spiders
How much a web vibrates affects how well a spider senses when that web has captured prey. But webs attached to concrete, plastic and other artificial materials vibrate less than do those built on natural materials, such as twigs or leaves.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentBurning to learn
Fires cause billions of dollars of destruction to homes and forests every year. But not all fires are bad, especially for forests. With a better understanding of fire, scientists can both help people prevent dangerous fires — and identify which ones it would be better to let burn.
-
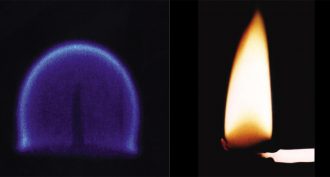 Environment
EnvironmentExplainer: How and why fires burn
A fire’s colorful flame results from a chemical reaction known as combustion.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPassing diseases from bee to bee
A study finds that the viruses and parasites that plague honeybees can infect bumblebees too, sickening another important pollinator.
-
 Animals
Animals‘Crazy’ ant fight
By neutralizing the poison produced by fire ants, ‘crazy’ ants can survive heated battles. And that may help explain why crazy ants are edging out fire ants in parts of the southern United States.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesArctic thaw is spreading wildlife diseases
Polar animals are encountering new, killer parasites as melting ice unlocks their access to new hosts.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA weekend for the birds
February 14 to 17 is this year’s Great Backyard Bird Count. It offers an opportunity to not only learn about the birds in your neighborhood but also contribute to science.
-
 Life
LifeCaught in the act
Scientists observe some evolutionary speed demons as they adapt over the course of just a few years to new environmental conditions.
-
 Animals
AnimalsExplainer: Animals’ role in human disease
Wildlife, livestock and pets are the source of most germs that can sicken people
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What should I know about HIV and AIDS?
Here are some common myths and some less common facts.
By Bryn Nelson