HS-LS2-6
Evaluate the claims, evidence, and reasoning that the complex interactions in ecosystems maintain relatively consistent numbers and types of organisms in stable conditions, but changing conditions may result in a new ecosystem.
-
 Life
LifeSome pikas survive winter by eating yak poop
Pikas endure bone-chilling cold on the Tibetan Plateau by using little energy and fueling up on yak poop.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSpiders can take down and feast on surprisingly big snakes
Snared in sticky webs and subdued by poison, even venomous snakes can become a spider’s soup.
By Asher Jones -
 Animals
AnimalsUrchin mobs can literally dis-arm a predator
Urchins are important herbivores — but not strict vegetarians. When hungry enough, they may even rip apart their predators for lunch.
By Jake Buehler -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsUrchin takeover underlies California’s vanishing kelp forests
Some 95 percent of kelp forests along its northern coast are gone. Meanwhile, sea otters are helping slow the loss of surviving kelp farther south.
-
 Climate
ClimateChanging climate now threatens northern lakes year round
Lakes in northern climes are getting warmer, and that’s not good for people, plants or animals.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesSome microbial hitchhikers may weaken body’s attack on COVID-19
New research identifies an altered mix of microbes in the body — ones commonly seen in people with poor diets — that may worsen coronavirus disease.
-
 Animals
AnimalsChoked by bacteria, some starfish are turning to goo
For years, researchers thought gooey, dying starfish were infected. Instead, these sea stars are suffocating. And bacteria may be behind it all.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentJumping ‘snake worms’ are invading U.S. forests
These bad-news invaders are spreading across the United States. As they turn forest debris into bare ground, soils and ecosystems are changing.
By Megan Sever -
 Plants
PlantsThe faster trees grow, the younger they die
As climate change spurs forest tree growth, it also shortens trees’ lives. That results in a quicker release of climate-warming carbon back into the atmosphere.
-
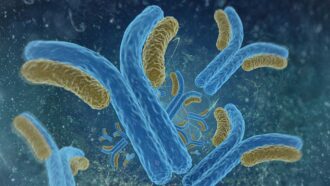 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA glowing new way to measure antibodies
Researchers invent a way to detect and measure antibodies with glowing proteins. Antibodies can mark exposure to various diseases.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsA single chemical may draw lonely locusts into a hungry swarm
Swarms of locusts can destroy crops. Scientists have discovered a chemical that might make locusts come together in huge hungry swarms.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAre coyotes moving into your neighborhood?
How do coyotes survive in New York City, Los Angeles and Chicago? Researchers and citizen scientists are working together to find answers.