HS-LS2-8
Evaluate the evidence for the role of group behavior on individual and species' chances to survive and reproduce.
-
 Animals
AnimalsExplainer: Male-female flexibility in animals
Some animals behave as if they were the opposite sex; others can even change their sex — and still produce offspring.
-
 Computing
ComputingThese young scientists are passionate about tech and math
The 2015 Broadcom MASTERS International delegates show why math and computer skills are key to the success of science-fair projects.
-
 Animals
AnimalsReturn of the bed bug
Bed bugs have staged a comeback over the past 15 years. The bloodsucking parasites succeeded through a combination of evolution and luck.
By Brooke Borel -
 Animals
Animals4 reasons not to ignore signs of bed bugs
Here are important reasons not to ignore signs of bed bugs. Above all, an infestation carries real risks to your health and wellbeing.
By Brooke Borel -
 Animals
AnimalsWhat’s for dinner? Mom.
Female spiders of one species make the ultimate sacrifice when raising their young: The mothers feed themselves to their children.
By Susan Milius -
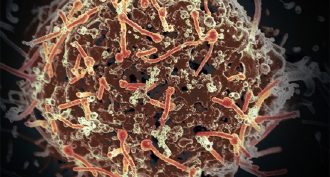 Microbes
MicrobesNews Brief: Ebola’s dead stay infectious for a week
The Ebola virus doesn’t die with its victims — at least not right away. A corpse may host live virus for up to a week after death, a new study finds.
By Janet Raloff -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMovies may tempt teens to drink
British 15-year-olds were more likely to binge-drink or have alcohol-related problems if they watched movies with plenty of onscreen drinking.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChickens spread latest deadly bird flu
A new bird flu virus threatens to spread outside of China. Experts traced the germ to markets where live chickens are sold.
-
 Plants
PlantsDesert plants: The ultimate survivors
Creosote, mesquite and other desert plants rely on different adaptations to thrive, even when no rain falls for an entire year.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPicture This: Winter brings white noses
White-nose syndrome, caused by a fungus, has killed millions of bats in the eastern United States. Now, scientists show that the disease comes and goes, by season. The finding could help scientists more effectively target any treatments.
-
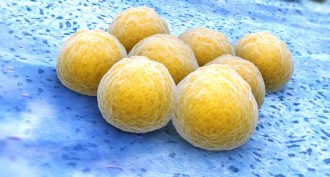 Microbes
MicrobesGerms help each other fend off antibiotics
Drug-resistant bacteria can cause persistent infections. A new study finds these germs fight drugs in different ways. And they can swap various compounds, increasing their neighbors’ chances of overcoming the drugs meant to kill them.
-

Food can make an appetizing science fair project
Many students think they need a laboratory or special equipment for a winning research project. But finalists at the Broadcom MASTERS competition showed food-based research may require little more than your home kitchen