HS-LS2-8
Evaluate the evidence for the role of group behavior on individual and species' chances to survive and reproduce.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMite-y discoveries!
Two teens from Russia discovered tiny mites living inside grass-like plants called rushes. Three of the species they turned up are new to science.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsMove over cheetah: Mite sets new speed record
A super-speedy species sprints faster than any other land animal — for its size, a new study finds. Scientists may someday tap this tiny mite’s technique to create robots and other devices that zip around at sensational speeds!
-
 Animals
AnimalsDon’t mess with a frustrated fish
When a trout doesn't get the snack it expected, look out. These fish get aggressive. Sometimes they can defeat even bigger fish.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineInfected cutting boards
Germs can hitchhike into the kitchen on meat and many types of produce. A new study finds that some of those germs are particularly nasty. They are immune to the one or more of the drugs doctors would prescribe to wipe out the infection.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese insects thirst for tears
In some parts of the world, insects will drop by for a savory beverage. Interestingly, neither a croc — nor a scientist who offered his eyes up to ‘tear-sipping’ bees — seemed bothered much by the freeloaders.
By Janet Raloff -
 Plants
PlantsWily bacteria create ‘zombie’ plants
Scientists have discovered how some plant pathogens ensure their own survival by transforming flowering plants into strictly leaf-producing ones. These green ‘zombies’ attract insects that the parasites need to help them spread to other plants.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhen a species can’t stand the heat
When temperatures rise, New Zealand’s tuatara produce more males. With global warming, that could leave the ancient reptile species with too few females to avoid going extinct.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPythons seem to have an internal compass
The giant, Burmese pythons living in Florida’s Everglades like their adopted home. And new research shows they can find their way back to it if people try to move them somewhere else. Not all snakes will do this.
By Susan Milius -
 Environment
EnvironmentBurning to learn
Fires cause billions of dollars of destruction to homes and forests every year. But not all fires are bad, especially for forests. With a better understanding of fire, scientists can both help people prevent dangerous fires — and identify which ones it would be better to let burn.
-
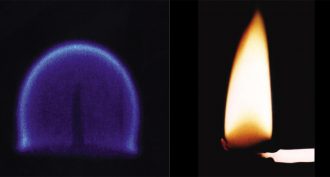 Environment
EnvironmentExplainer: How and why fires burn
A fire’s colorful flame results from a chemical reaction known as combustion.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIntel STS finalist finds new flu fighters
Intel Science Talent Search finalist Eric Chen used a computer simulation to narrow down chemical targets to fight influenza. The drugs that he identified could be the next big weapons against flu.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPassing diseases from bee to bee
A study finds that the viruses and parasites that plague honeybees can infect bumblebees too, sickening another important pollinator.